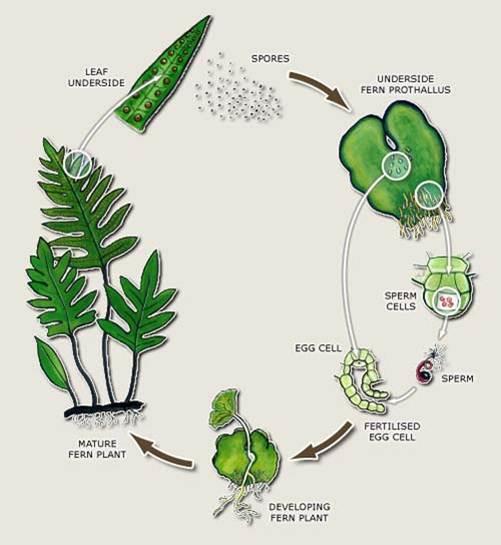
Most ferns reproduce through spores found underneath leaves When mature, the spores explode and release a dark brown, dustlike substance When this comes in contact with warm and moist soil, the process of reproduction begins When the humidity, light and temperature is ideal, new fern plants growIn the sexual mode of reproduction, new plants are produced through the fusion of female and male gametes which forms the embryo This fusion of gametes gives rise to the seed which is the site that would bear the new plant structures in the futurePlants can reproduce either sexually (through spores or seeds) or asexually (vegetatively) There is a geographic pattern to plant reproduction in the temperate zones of the world, cold winters make it difficult for plants to reproduce vegetatively, while in the tropics vegetative reproduction is an option for both wild and cultivated plants

Learning By Questions
Plant reproduction through seeds
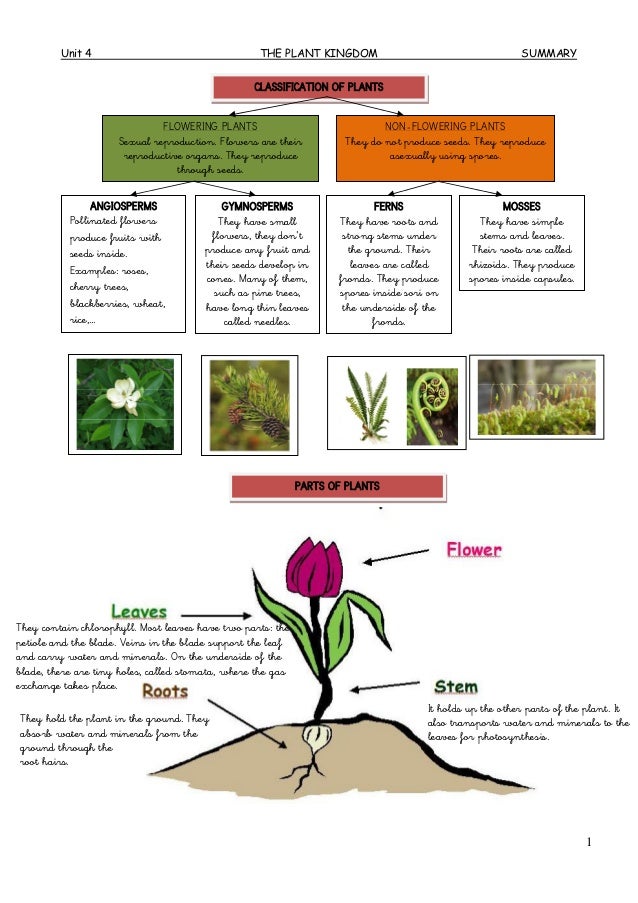
Plant reproduction through seeds- There are several ways by which plants produce their offspring These are categorised into two types (i) asexual, and (ii) sexual In asexual reproduction plants can give rise to new plants without seeds, whereas in sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seedsModes Of Reproduction In Plants In plants, reproduction is carried out via two modes Asexual Mode – New plants are obtained without producing seeds;




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii
Non Seed Plants Seed Plants PLANT REPRODUCTION HOW TO CLASSIFY HUGUET FITÉ, Janet CEIP Antoni Roig Name _____ Revision activity 1 Use the information from the boxes to complete the questions through colour and scent Corolla Receives the pollen from the antherIn flowering plants, the term "apomixis" is commonly used in a restricted sense to mean agamospermy, ie, clonal reproduction through seeds Although agamospermy could theoretically occur in gymnosperms, it appears to be absent in that group Apogamy is a related term that has had various meanings over time Asexual reproduction produces individuals that are genetically identical to the parent plant Roots such as corms, stem tubers, rhizomes, and stolon undergo vegetative reproduction Some plants can produce seeds without fertilization via apomixis where the ovule or ovary gives rise to new seeds
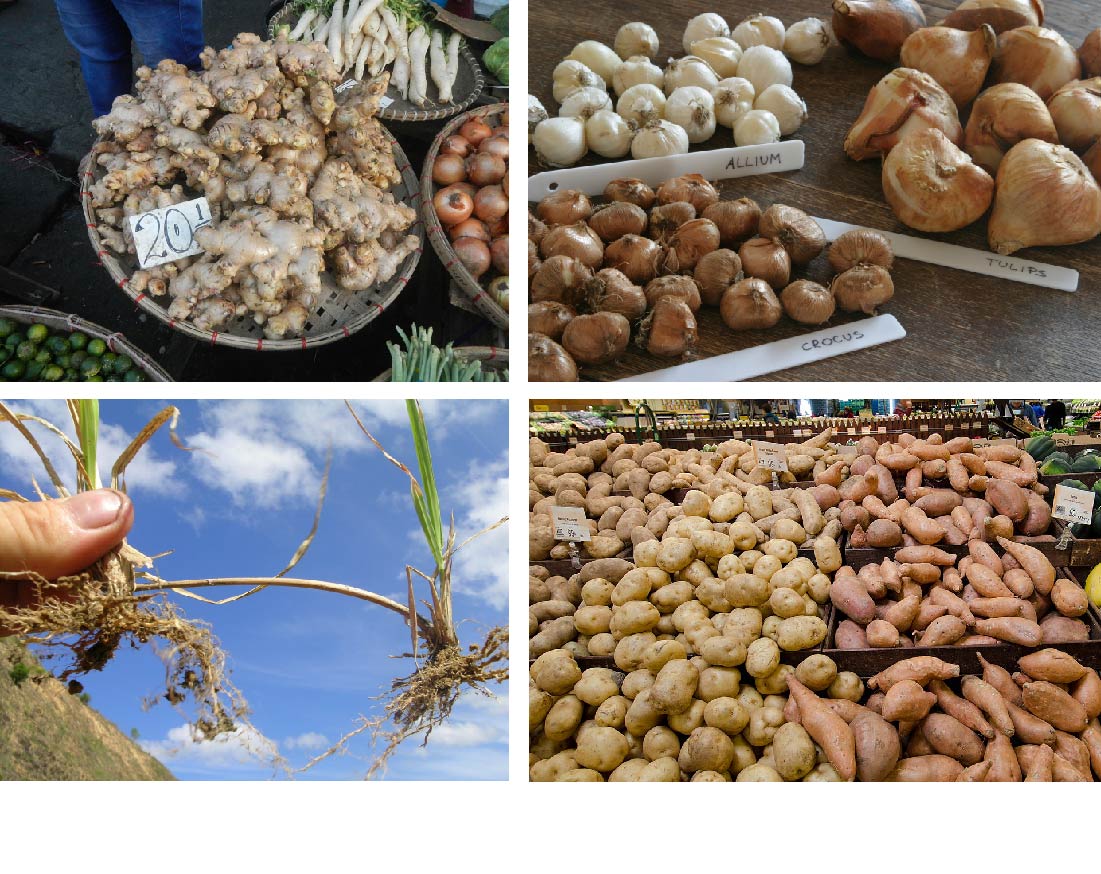
Therefore, the saffron crocus has to reproduce via corms A corm, much like bulbs of tulips, are a top shaped structure that is planted underground instead of seeds From this mass of cells, the saffron plant can grow and then take "breaks" underground by continually living through Reproduction in plants occur via two modes asexual and sexual Asexual mode of reproduction includes, vegetative propagation, budding, fragmentation and spore formation Vegetative propagation occurs through vegetative parts of the plant It can also be done by artificial methods Plant reproduction comes in two types sexual and asexual Sexual reproduction is similar to human reproduction, in which male pollen and female ovarian germ cells fuse into a new organism that inherits the genes of both parents The sexually reproductive part of a plant is the flower Asexual reproduction involves vegetative reproduction through stems, roots, and leaves
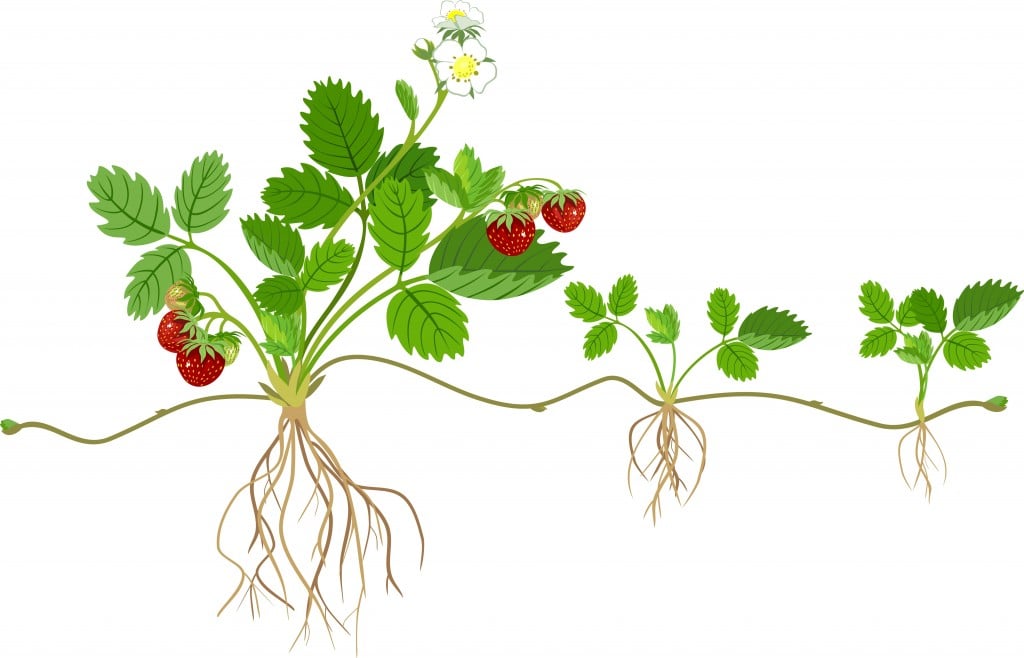
Genetically identical to all others in the same colony However, in vegetative reproduction, the new plants that result are new individuals in almost every respect except genetic makeup The effect of altered bird species composition and abundance on seed dispersal was associated with a 74% reduction in seed dispersal for P crassifolium Additionally, undispersed seeds of P crassifolium had lower germination, and higher predispersal seed predation, compared with dispersed seeds We stress three important aspects of these results (1) for some plant species, the same bird species perform both pollination and seed dispersal, (2) dispersal reduces predispersal seed Plant reproduction without seeds Not every plant grows from a seed Some plants, like ferns and mosses, grow from spores Other plants use asexual vegetative reproduction and grow new plants from rhizomes or tubers We can also use techniques like grafting or take cuttings to make new plants




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express



Flowering Plant Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction in Plants Plants can reproduce asexually or sexually But the majority of the flowering plants reproduce sexually The flower is the reproductive part of a plant ie, both male and female gametes are produced by flowers Sexual reproduction in plants takes place in flowers During sexual reproduction, they produce seeds Seeds produced through fertilization contain genetic material from both parents As a result, the offspring are not genetically identical to either of the parent plants This genetic diversity can help them survive if the environment changes Flowering plants reproduce sexually through a process called pollinationAnswer (1 of 12) Common Snapdragon also known to be Antirrhinum majus common snapdragon is from figwort family It is fast growing plant and that attracts Humming birds Flower can be any color except blue and size range from 3 Feet to 4 inches tall PLant a




Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow
Some reproduce through spores and some through seeds Source 4bpblogspotcom Flowering plants reproduce asexually through runners and underground stems Some reproduce through spores and some through seeds Seedless vascular plants went on to dominate the land through the carboniferous period, about 300 million years ago The video explains how plants reproduce through seeds It shows how seeds germinate and what are required for germination It also explains the importance ofThe video explains how plants reproduce without a seed like potato plant reproduce from stem, strawberry reproduce from runner, few plants can reproduce from
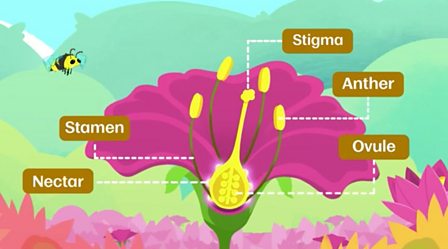



How Do Flowering Plants Reproduce c Bitesize




Ppt Chapter 24 Reproduction Of Seed Plants Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Vegetative propagation or vegetative reproduction is the growth and development of a plant by asexual means This development occurs through the fragmentation and regeneration of specialized vegetative plant parts Many plants that reproduce asexually are also capable of sexual propagation The primary distinction between seed plants and seedless plants is that seedless plants do not hold propagation seeds, while seed plants do not carry propagation seeds The spores are produced by seed plants through sexual reproductionTry vegetative propagation using several different parts of the plant, such as a piece of stem, a piece of root, a leaf (with no stem), an leaf with some stem, and the tip of a leaf Place a toothpick on either side of your plant part (or in the case of the leaf, put the toothpick right through it)




Learning By Questions




Plant Asexual Reproduction Educational Video For Kids Youtube
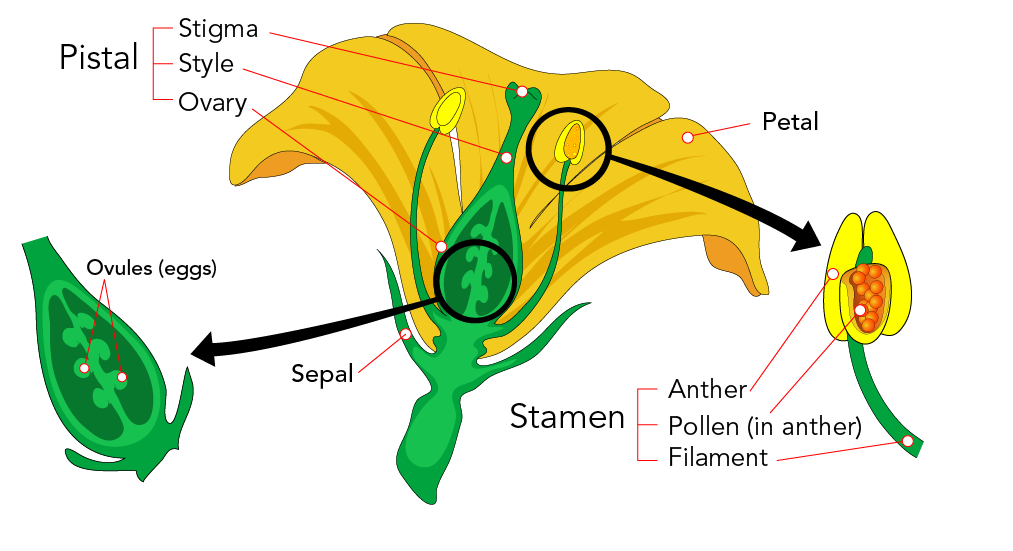
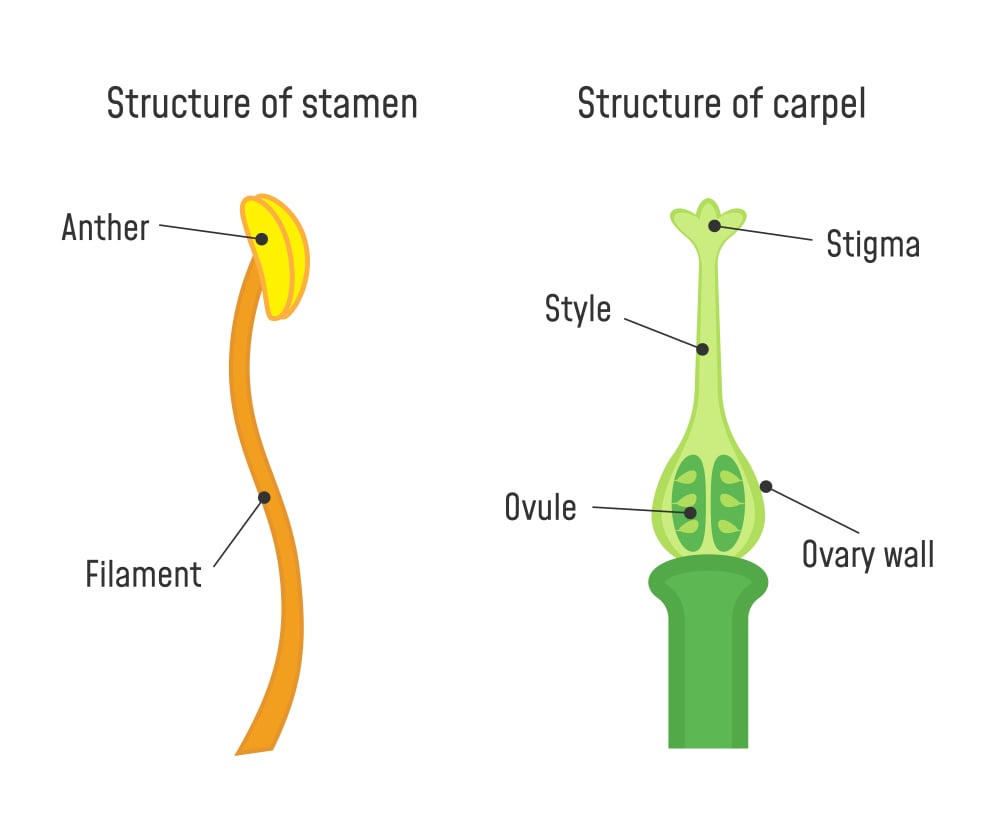
Sex organs of plants are found inside flowers A male reproductive organ is called as Androecium and a female sex organ is called as Gynoecium Androecium has following parts (i) Filament (ii) Connective, and (iii) Pollen Sac Filament is a thread like structure which bears pollen grain through connective and the base of the flowerFlowering plants, the angiosperms, were the last of the seed plant groups to evolve, appearing over 100 million years ago during the middle of the Age of Dinosaurs (late Jurassic) All flowering plants produce flowers and if they are sexually reproductive, they produce a diploid zygote and triploid endospermAll plants can reproduce through seeds, except for those hybrids/cultivars that are so radically modified that they have lost reproductive function Seedless watermelon and hybrid tea roses would be examples of those that CANNOT reproduce form seed




Science Plant Reproduction Seed Dispersal Germination English Youtube




Ks2 Reproduction How Do Plants Make And Disperse Seeds
A plant that persists in a location through vegetative reproduction of individuals constitutes a clonal colony;Roots such as corms, stem tubers, rhizomes, and stolon undergo vegetative reproduction Some plants can produce seeds without fertilization via apomixis where the ovule or ovary gives rise to new seeds Advantages of asexual reproduction include an increased rate of maturity and aAsexual reproduction in plants occurs in two fundamental forms vegetative reproduction and agamospermy Vegetative reproduction involves a vegetative piece of the original plant (budding, tillering, etc) and is distinguished from apomixis, which is a replacement of sexual reproduction, and in some cases involves seeds




Plant Reproduction Bioninja



Grade 4 Science Lesson 5 Plant Reproduction Primary Science
Plants without seeds, whereas in sexual Asexual reproduction In asexual reproduction new plants are obtained without production of seeds Vegetative propagation It is a type of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced from roots, stems, leaves and buds Since reproduction is through the vegetative parts of the plant, it is known asSome plants can reproduce sexually & asexually because some plants reproduce sexually through flowers and reproduce asexually through the different parts of the plant without the flower having a role in this process and the resulting individuals are completely identical to the original plant Pollination in palm trees is artificial pollination because it takes place by man Flowering plants, often known as angiosperms, reproduce in a sexual manner Plant reproduction is primarily centered on the flower, which contains both male and female gametes Although some components of flowers are sterile, but they all help in the reproduction process Angiosperms' reproductive organs are found in the flower




Plant Reproduction Wikipedia



1
Plants that reproduce from spores Spores are different to seeds They do not contain plant embryos or food stores When the sporangia break open, the spores are released and dispersed by the wind If the spore lands in a suitable environment, it can grow into a tiny plant called a gametophytePlant reproductive system, any of the systems, sexual or asexual, by which plants reproduce Asexual reproduction results in offspring that are identical to the parent plant Sexual reproduction involves new genetic combinations and results in offspring that are genetically different from the parent plantsPlant reproduction is the process by which plants generate new individuals, or offspring Seed produced through selfpollination ("selfed" seed) is often inferior in growth, survival, and fecundity to seed produced through outcross pollination ("outcrossed" seed) As a result, in most species there is strong natural selection to maximize




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica
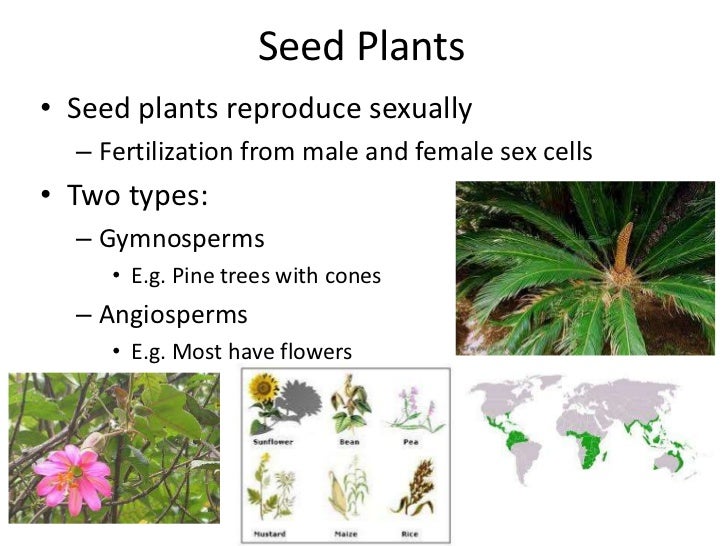



Plant Reproduction Seed Plants
The simple definition of apomixis (see Glossary), asexual reproduction through seeds 1,2, conceals its complex developmental underpinnings that include pathways of meiosis (and its avoidance, apomeiosis), embryo formation from unfertilized cells gametic (parthenogenesis) or sporophytic (adventitious embryony), and nutritive tissue development to support embryo Sexual reproduction flowering plants make use of seeds In most plants, the seedlings are developed from their seeds, which is obtained from flower when the male and female parts of flower meet to form union, seeds are obtained from flower Asexual or Vegetative Reproduction the use of vegetative parts of plants (leaves, stems, buds and roots) Asexual reproduction may occur through Binary Fission, budding, fragmentation, spore formation, Regeneration and vegetative propagation Plants have two main types of asexual reproduction in which new plants are produced that are




Loh Pei Hang D 2 3 Plants Reproduce
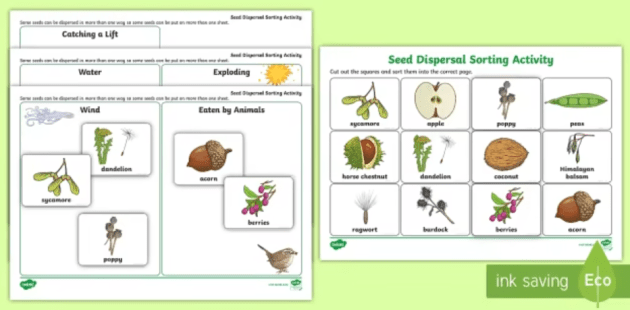



What Is Reproduction In Plants Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki
Reproduction by Hibiscus Seeds In the wild, hibiscus species reproduce sexually when pollen from male flowers reaches female flowers forSexual Mode – New plants are obtained from seeds Asexual Reproduction In Plants In asexual reproduction in plants, plants are reproduced without the formation of seeds Following are a few ways in which plants reproduceThe process of pollination is aided by many agents of pollination such as wind or insects which take pollen grains to other rose plants (in case of crosspollination) After fertilization, embryo formation takes place This embryo is present in the seeds of the plant
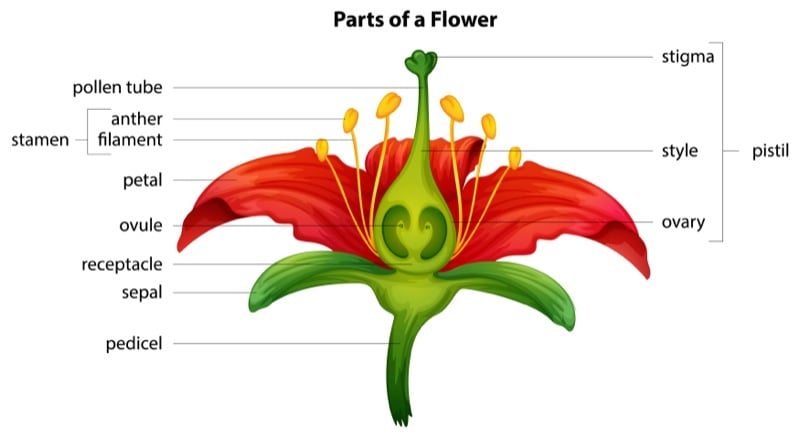



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce




Arizona Beetles Bugs Birds And More February 19




Germination And Growth In Plants Year 8 Lesson Powerpoint Ks3 8be Plant Reproduction Teaching Resources




Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants S Cool The Revision Website




Plant Reproduction Plants




Pdf Apomixis In Plant Reproduction A Novel Perspective On An Old Dilemma Semantic Scholar
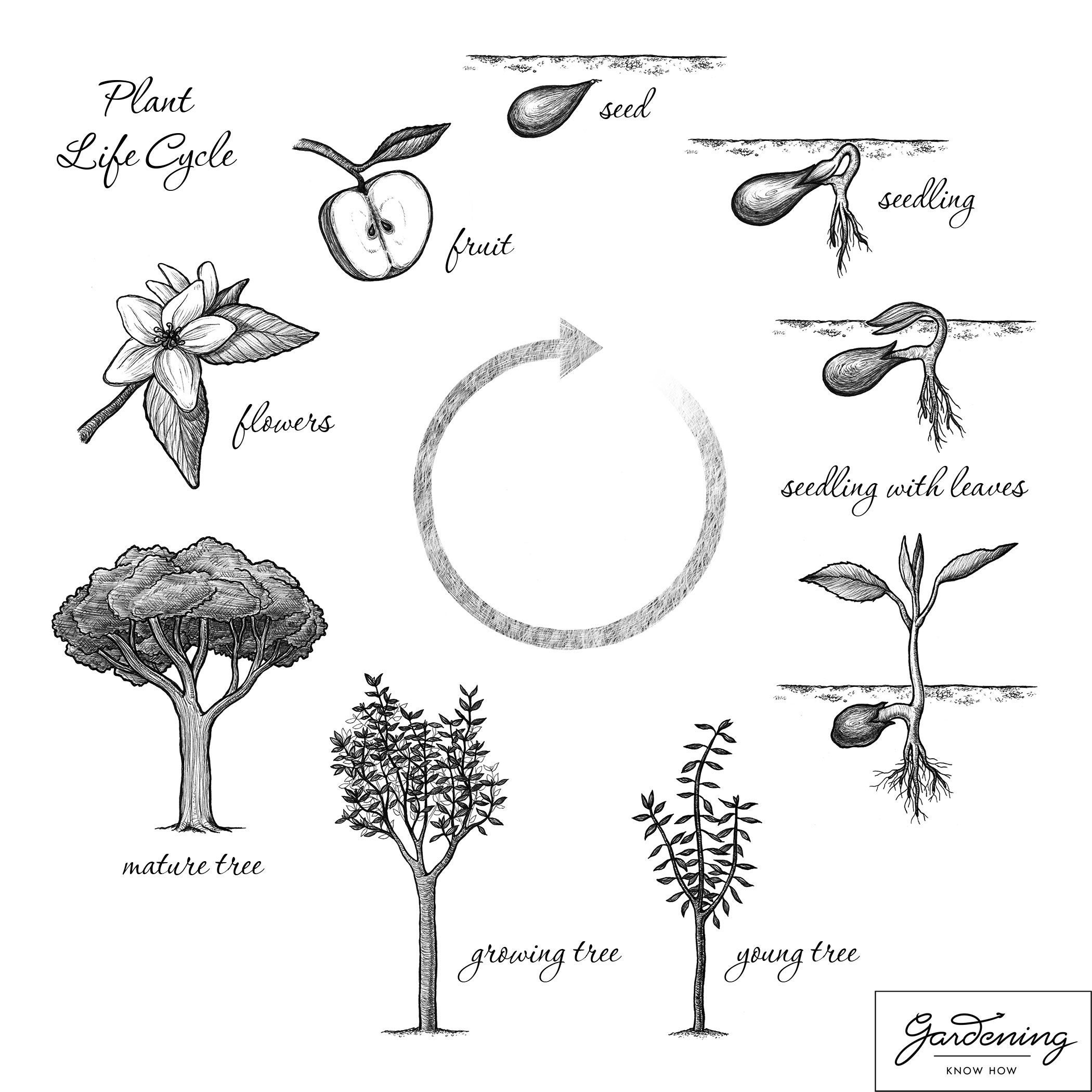



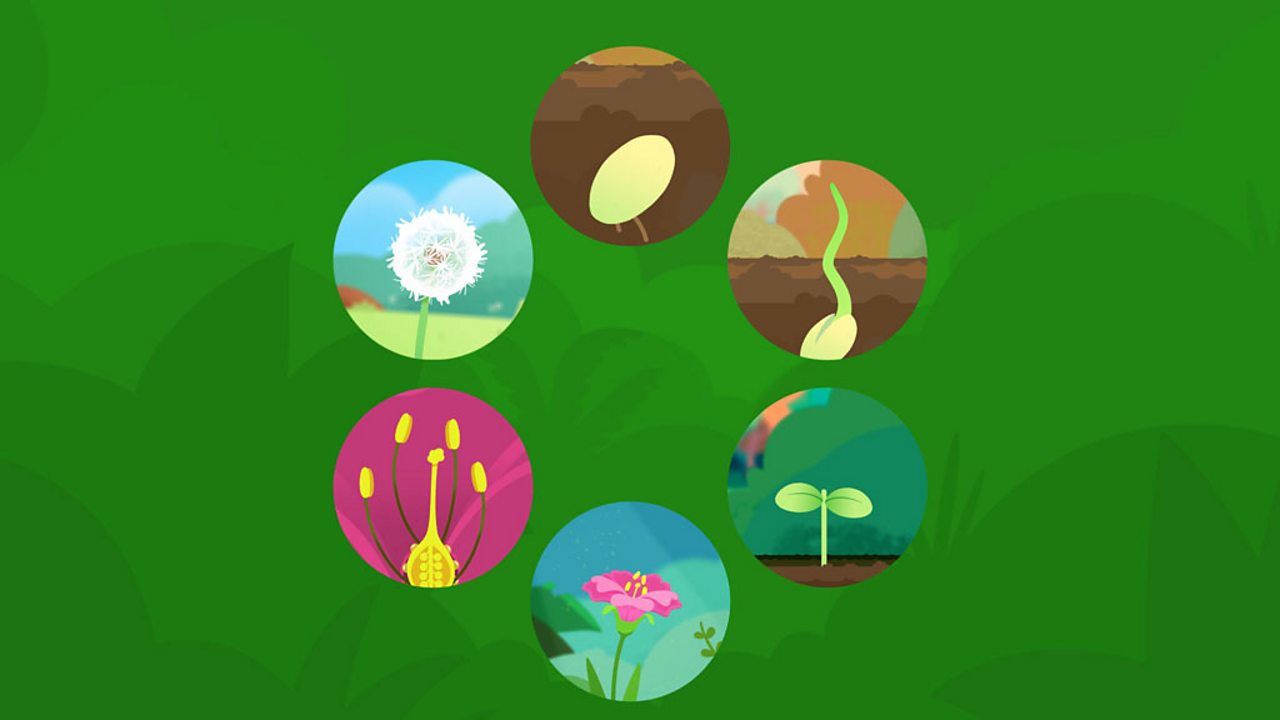
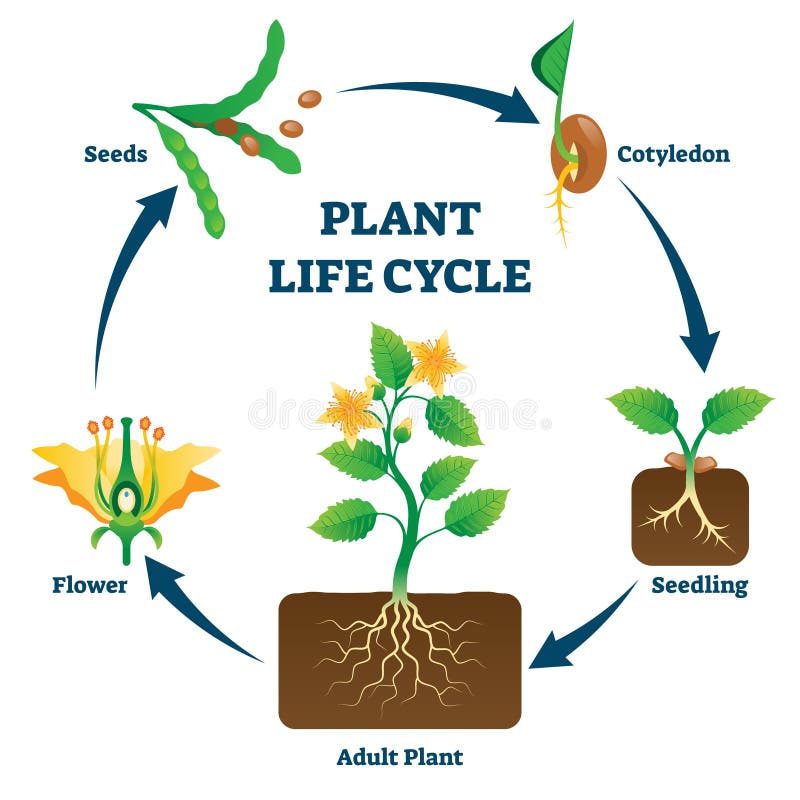
Basic Plant Life Cycle And The Life Cycle Of A Flowering Plant Gardening Know How




How Cone Bearing Plants Reproduce Students Britannica Kids Homework Help




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow




Vegetative Reproduction In Plants Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Stamen Definition Description Facts Britannica
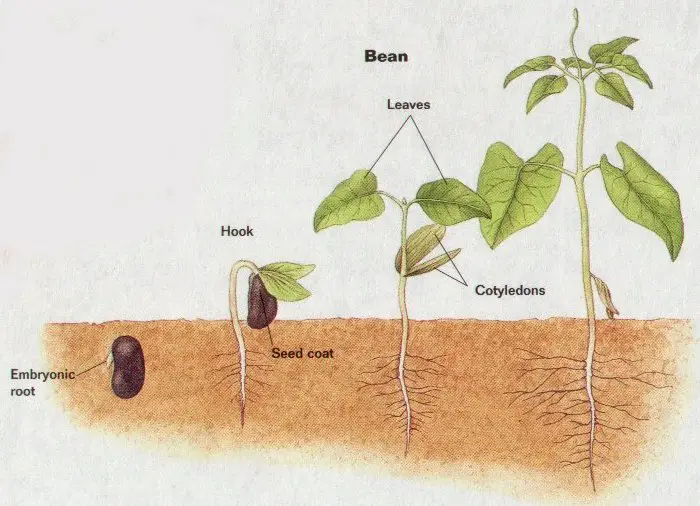



Plant Reproduction Biology Junction
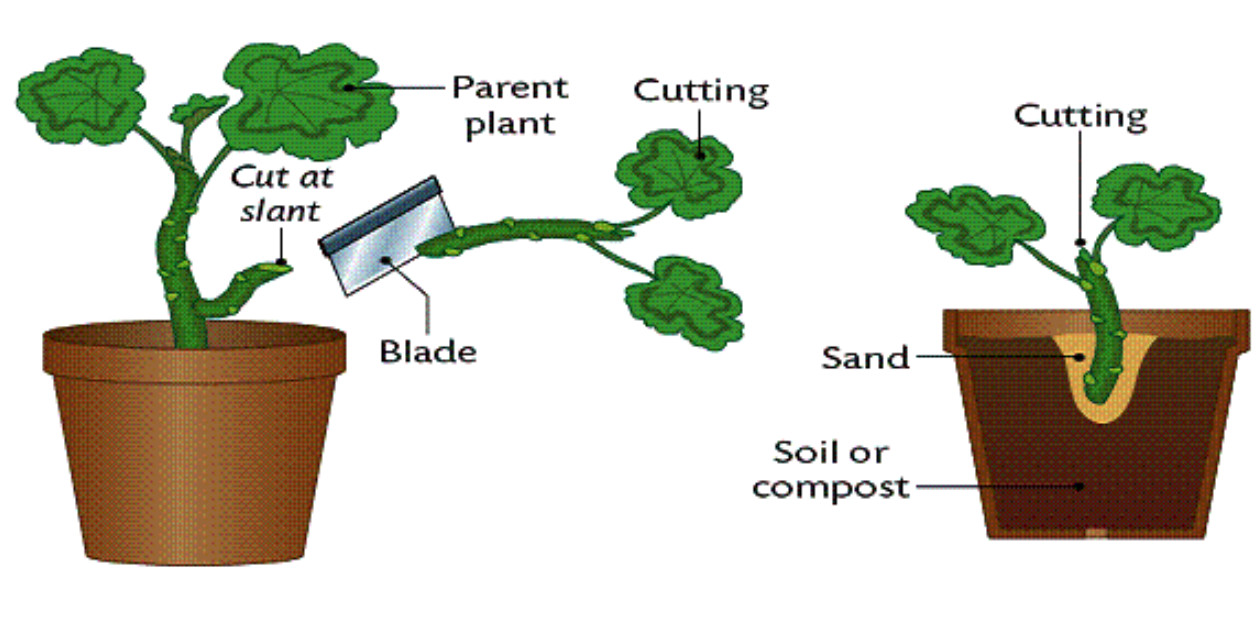



Asexual Reproduction In Plants Class 7 Reproduction In Plants Science




Plant Reproduction Lesson For Kids Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
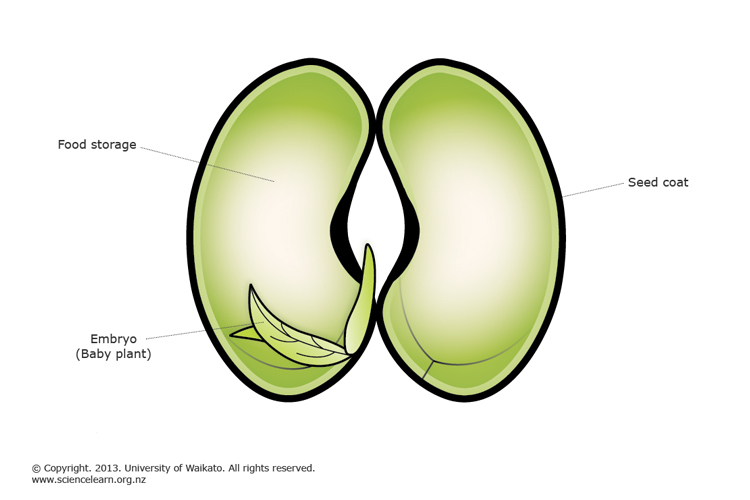



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Flowering Plants The Birds And The Bees And A Little Sneeze Hudsonalpha Institute For Biotechnology




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Fruits Flowers And Seeds Biology Online Tutorial



Ways Of Reproduction In Plants
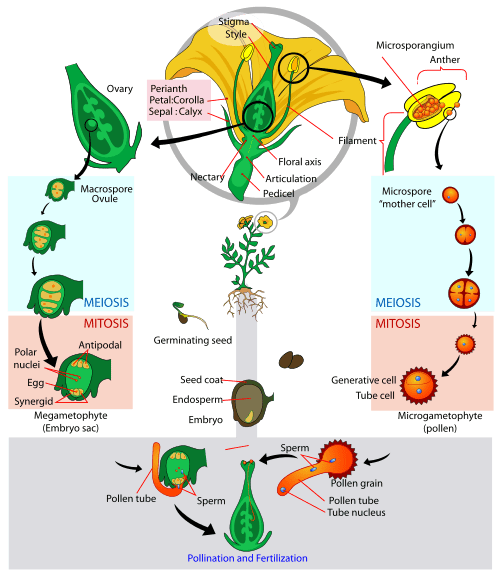



Plant Reproduction Organismal Biology



1




Plant Reproduction Sexual And Asexual Teaching Resources




Fun Germination Facts For Kids




Plant Fertilization Process Definition Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Plant Reproduction
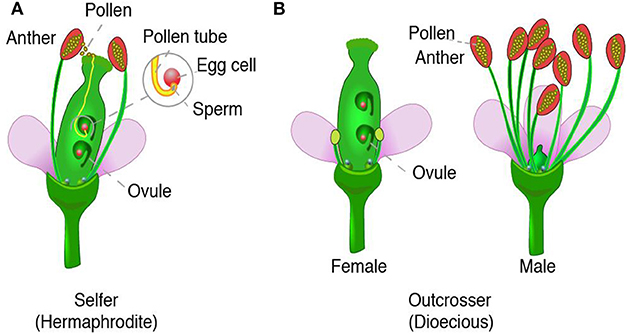



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds




Seeds And Flowers Plant Reproduction Plants Without Seeds




Plant Reproduction Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
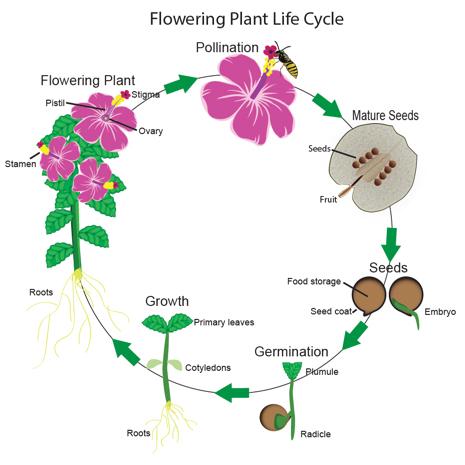



Flowering Plants Life Cycle Lovetoknow



What Plants Reproduce Through Seeds Give Two Examples Quora



1




Vegetative Reproduction Wikipedia




Reproduction In Plants Teaching Resources



Introduction To Reproduction Plants Animals Types Videos Examples




The Field Guide To Gymnosperms And Angiosperms Earth Com




Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce



1




Types Of Reproduction In Plants Youtube



Ginseng Reproduction




Seeds Science With Spence




How Plants Are Classified Part 2 Reproduction Ppt Download
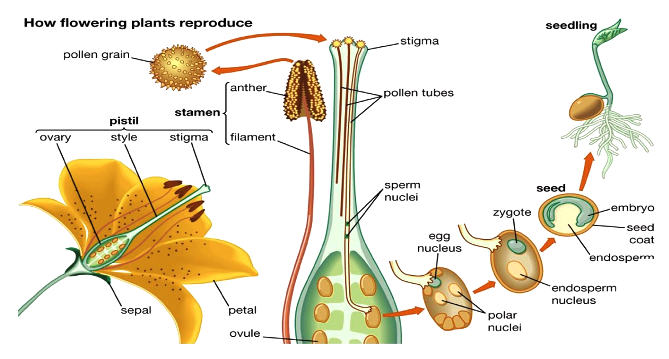



Learn About Flowering Plant Reproduction Chegg Com




Reproduction System Reproduction Systems In Plants Seed Propagated
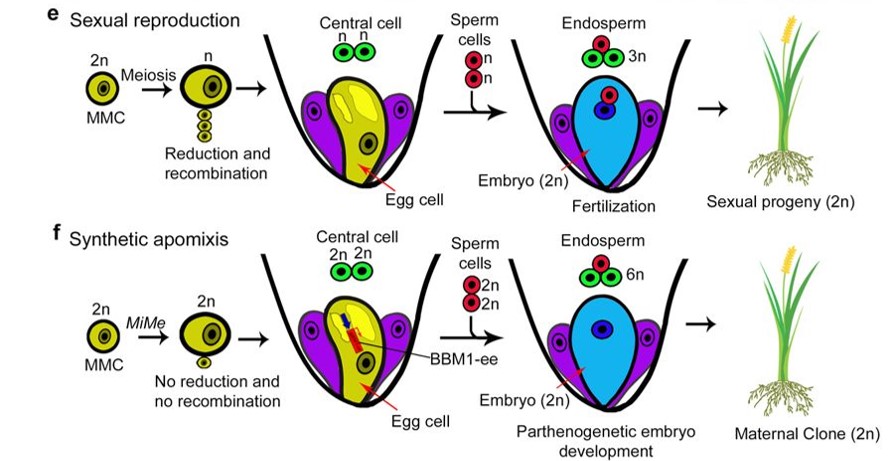



Plantae Synthetic Apomixis Asexual Propagation Through Seeds Nature Plantae



How Do Plants Reproduce Sexually B4fa



Tomatosphere Tomatosphere The Life Cycle Of A Tomato Plant




Science Unit Plants Concept Kinds Of Plants Ppt Video Online Download
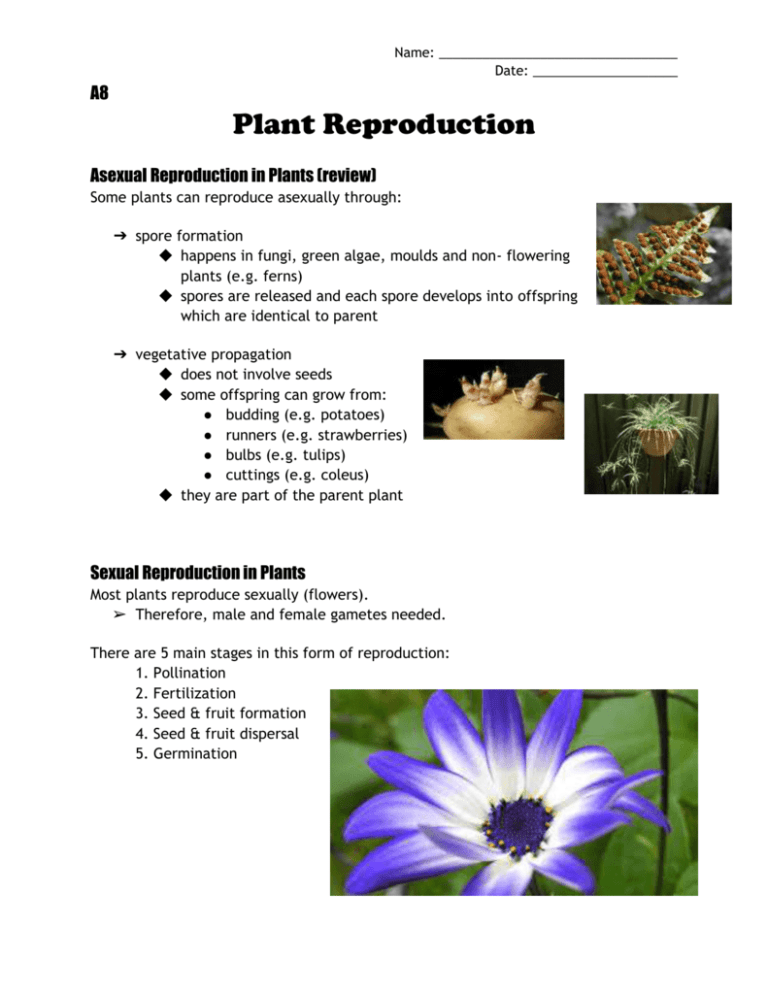



12 Plant Reproduction
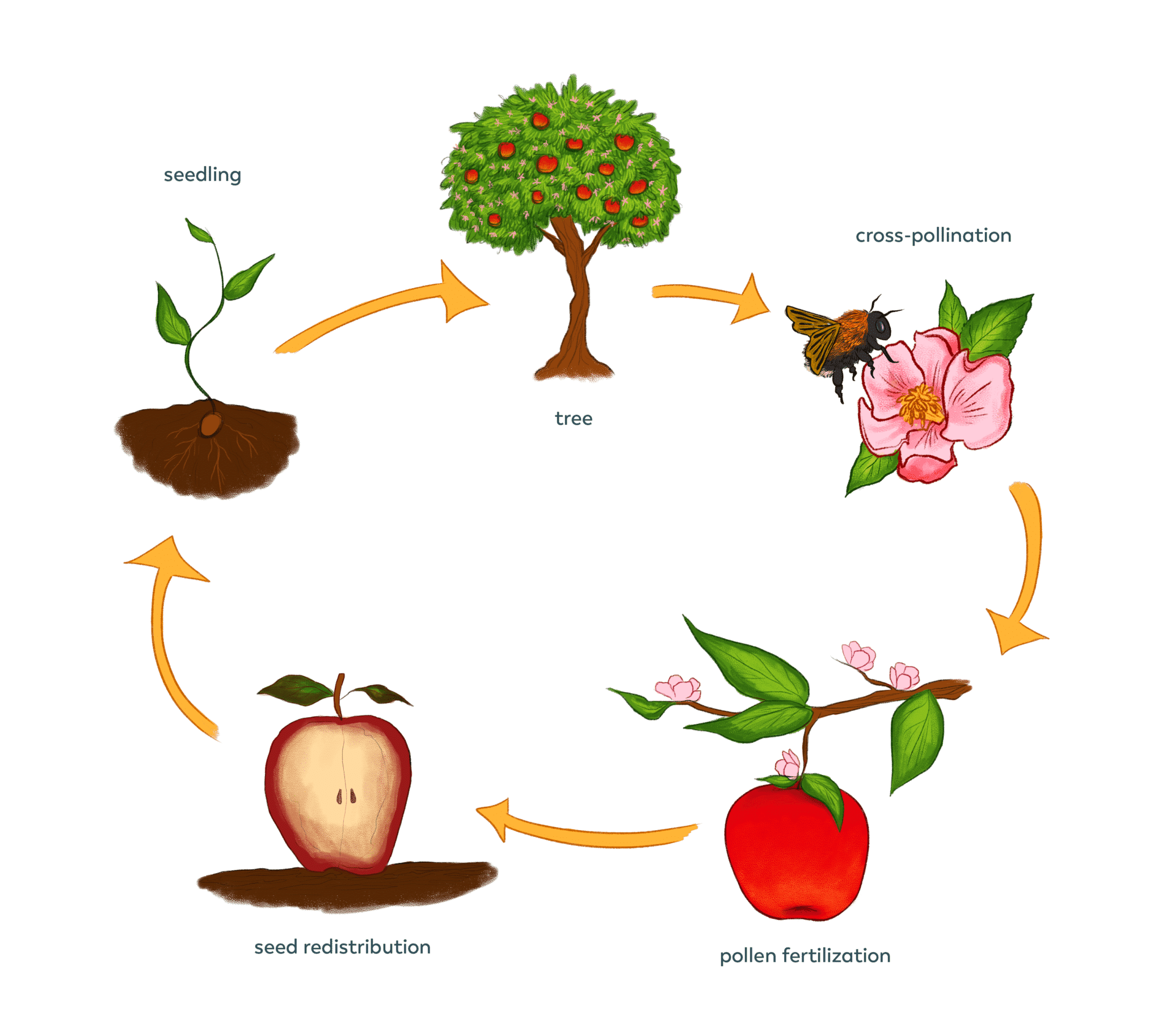



Pollination Pollinator Quest



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce




Plants Without Seeds Plant Reproduction Dk Find Out



Seeds Vs Seedless Plants Biology Socratic



Asexual Reproduction Biology Ii




This Is How Bananas Reproduce And How You Can Grow Them From Seed Happysprout




Science Plant Reproduction Seed And Germination Hindi Youtube




Flower Dissection Activity Review There Are Two Types Of Plants Plants With Seeds And Plants Without Seeds Ppt Download




Plant Reproduction Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Vegetative Reproduction Wikipedia



Unit 4 Diagram




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Reproduction In Plants Class 5 Youtube



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants




What Are The Stages Of A Plant S Life Cycle c Bitesize




7 790 Plant Reproduction Stock Photos And Images 123rf



Plant Reproduction Stock Illustrations 1 536 Plant Reproduction Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Plants Reproduction Hand Out




Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub




Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub
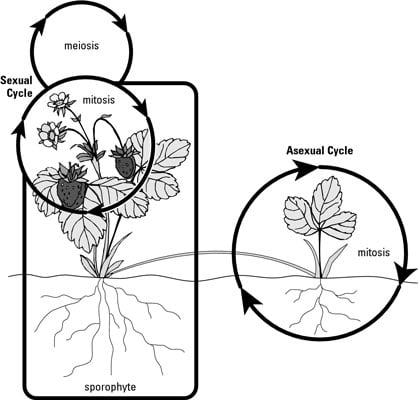



Plant Reproduction Dummies
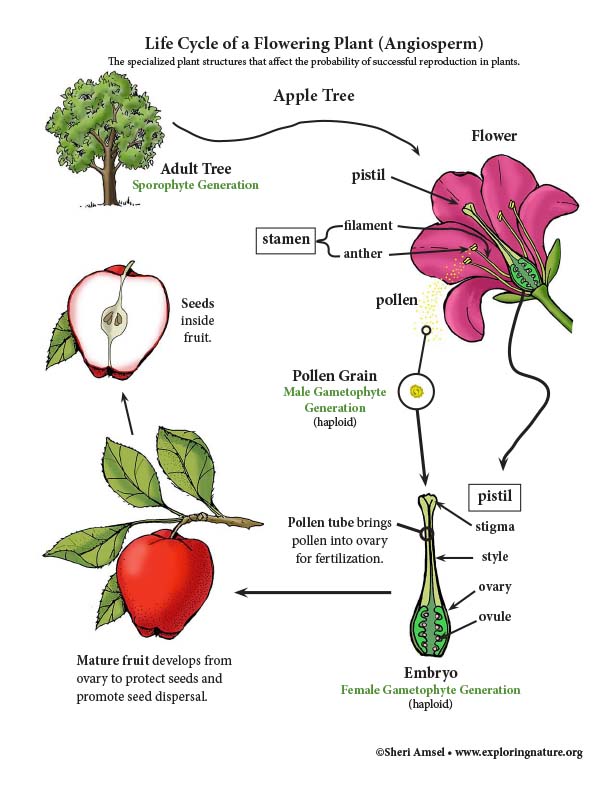



Plant Reproduction Illustrated Growth And Development Of Organisms Ngss 6 8 Grade




Igcse Plant Reproduction
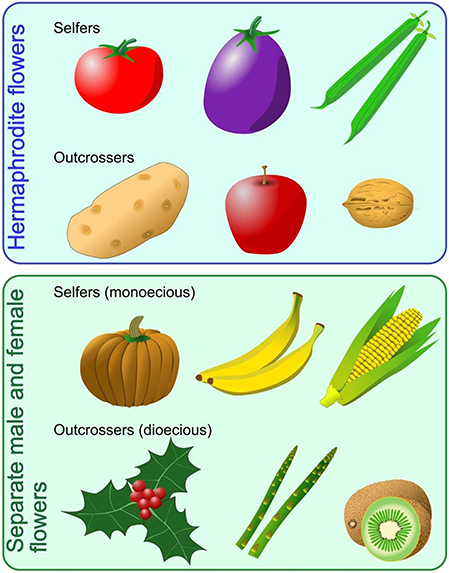



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds



Plant Reproduction Epic Science



Sexual Reproduction In Plants With Seeds Free Stories Online Create Books For Kids Storyjumper




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow




9 3a Plant Reproduction I Am So




Ppt Plant Reproduction Seed Plants Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Flower Dissection Activity Review There Are Two Types Of Plants Plants With Seeds And Plants Without Seeds Ppt Download



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants




School Learning Zone Plant Life Cycles



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿