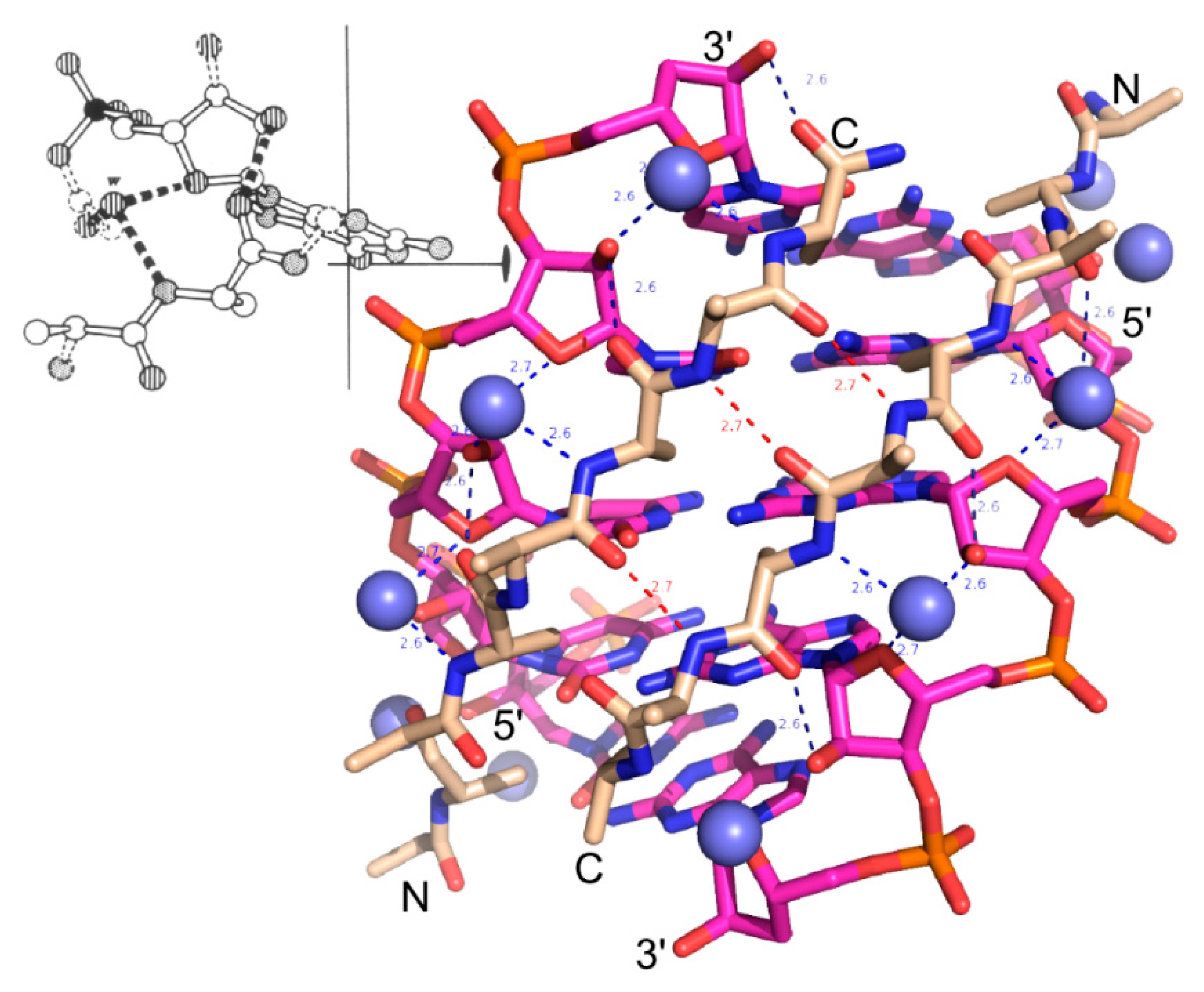
An RNA triple helix consists of three strands A Watson–Crick RNA double helix whose majorgroove establishes hydrogen bonds with the socalled "third strand"In the past 15 years, it has been recognized that these majorgroove RNA triple helices, like singlestranded and doublestranded RNA, also mediate prominent biological rolesThe specialized ribonuclease Dicer initiates RNA interference by cleaving doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) substrates into small fragments about 25 nucleotides in length InExamples include the packaging of dsRNA viral genomes into capsids, deformations of the ribosome during translation (1, 2), and more generally conformational changes of functional RNAs while folding or due to interactions with proteins (3, 4)
1
Why is rna not double stranded
Why is rna not double stranded- The specialized ribonuclease Dicer initiates RNA interference by cleaving doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) substrates into small fragments about 25 nucleotides in length In the crystal structure of anHowever, whereas DNA molecules are typically long and double stranded, RNA molecules are much shorter and are typically single stranded RNA molecules perform a variety of roles in the cell but are mainly involved in the process of protein synthesis (translation) and its regulation RNA Structure RNA is typically single stranded and is made of ribonucleotides that are linked by



What Is The Difference Between Dna And Double Stranded Rna Quora
Members of the ribonuclease III (RNase III) family are doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) specific endoribonucleases characterized by a signature motif in their active centers and a twobase 3′ overhang in their products Structure of the doublestranded RNAbinding domain of the protein kinase PKR reveals the molecular basis of its dsRNAmediated activation Sambasivarao Nanduri Structural Biology Program, Lerner Research Institute, The Cleveland Clinic Foundation, 9500 Euclid Avenue, Cleveland, OH, USA RNA can form into doublestranded structures, such as during translation, when mRNA and tRNA molecules pair DNA polymers are also much longer than RNA polymers;
Structural basis for cytosolic doublestranded RNA surveillance by human oligoadenylate synthetase 1 Jesse Donovan, Matthew Dufner, and Alexei Korennykh1 Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ Welcome to the Predict a Secondary Structure Web Server The Predict a Secondary Structure server combines four separate prediction and analysis algorithms calculating a partition function, predicting a minimum free energy (MFE) structure, finding structures with maximum expected accuracy, and pseudoknot predictionThis server takes a sequence, either RNA or Primary Citation of Related Structures 2LJH PubMed Abstract Adenosine deaminases that act on RNA (ADAR) catalyze adenosine to inosine (AtoI) editing in doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) substrates Inosine is read as guanosine by the translation machinery;
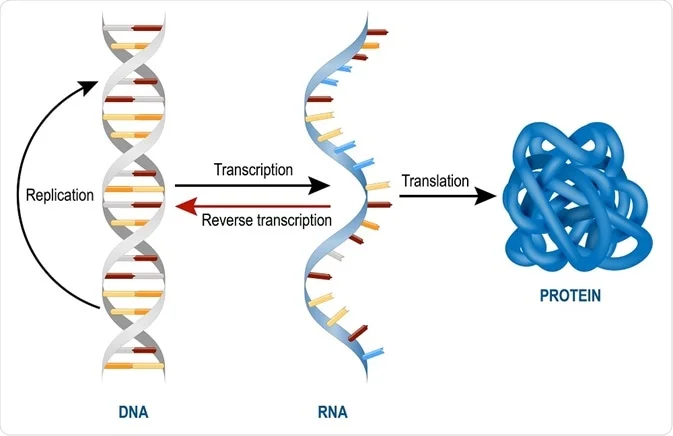
We describe four monoclonal antibodies (MAB) which specifically recognize doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) together with their use in new methods for detecting and characterizing dsRNA in unfractionated nucleic acid extracts The specificity of the antibodies was analyzed using a panel of 27 different synthetic and naturally occuring nucleic acidsWe present the first solution structures of the doublestranded RNAbinding domains (dsRBDs), dsRBD1 and dsRBD2, from mouse RHA We discuss the binding mode of the dsRBDs of RHA, in comparison with the known dsRBD structures in their complexesRNA is formed when the two strands of doublestranded DNA are separated, and one of the two strands is used as the template for RNA, with each DNA base used to inform the 'copying enzyme' (polymerase) which complementary base pair to add (A always pairing with T, C with G)




The Essential Role Of Double Stranded Rna Dependent Antiviral Signaling In The Degradation Of Nonself Single Stranded Rna In Nonimmune Cells The Journal Of Immunology




Tdp 1 The Caenorhabditis Elegans Ortholog Of Tdp 43 Limits The Accumulation Of Double Stranded Rna The Embo Journal
Structural Features Bform double helix DNA is a doublestranded molecule consisting of a long chain of nucleotides Aform helix RNA usually is a singlestrand helix consisting of shorter chains of nucleotides Composition of Bases and Sugars deoxyribose sugar phosphate backbone adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine bases ribose sugar Threedimensional structure of a protozoal doublestranded RNA virus that infects the enteric pathogen Giardia lamblia J Virol 11–1194 Crossref PubMed Google Scholar 32 Emsley P, Lohkamp B, Scott WG, Cowtan K 10 Features and development of Coot Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr –501Green and Mathews, 1992;



Life Free Full Text What Rna World Why A Peptide Rna Partnership Merits Renewed Experimental Attention Html




The Essential Role Of Double Stranded Rna Dependent Antiviral Signaling In The Degradation Of Nonself Single Stranded Rna In Nonimmune Cells The Journal Of Immunology
RNA interference (RNAi) is a genetic regulatory system that functions to silence the activity of specific genes RNAi occurs naturally, through the production of nuclearencoded premicroRNA (premiRNA), and can be induced experimentally, using short segments of synthetic doublestranded RNA (dsRNA)The EMBO Journal Vol17 No24 pp7505–7513, 1998 Molecular basis of doublestranded RNA–protein interactions structure of a dsRNAbinding domain complexed with dsRNA Jodi MRyter1 and Steve CSchultz2 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Colorado, In many of these contexts, structures rich in doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) helices encounter mechanical strains;




10 Replication Of Dsrna Virus Youtube




Structures And Axis Curves For Ideal Dsdna And Dsrna Left Dna Right Download Scientific Diagram
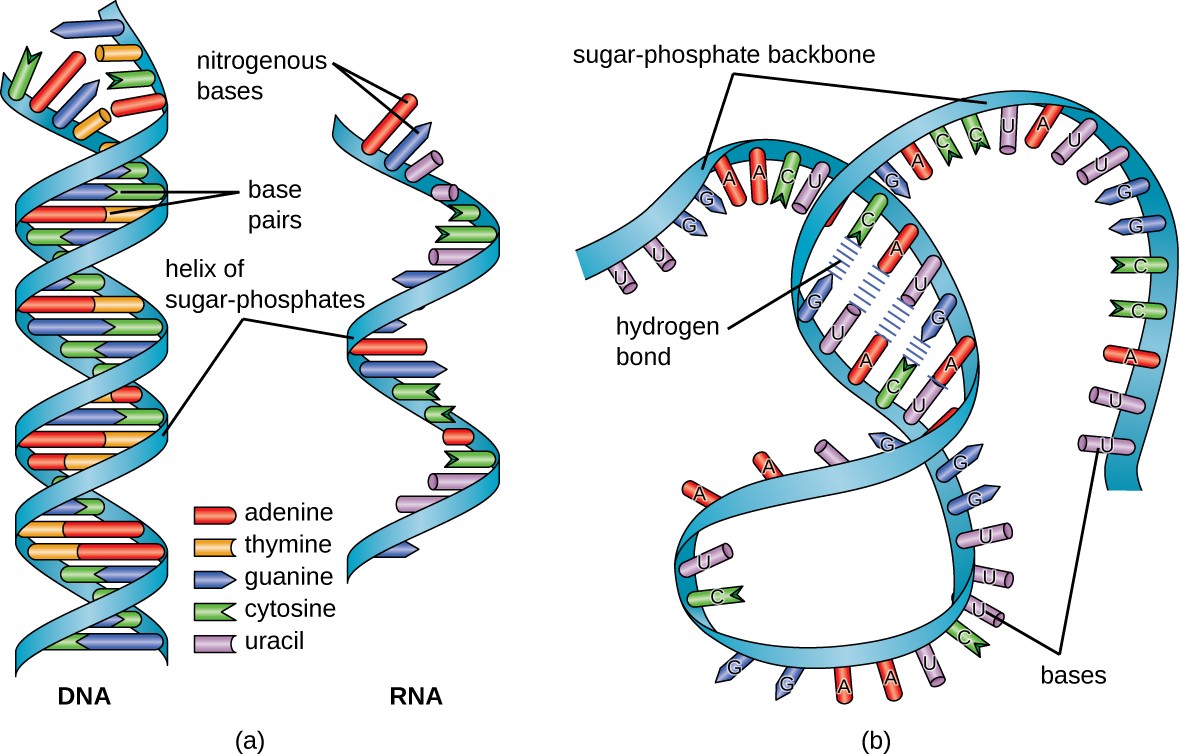
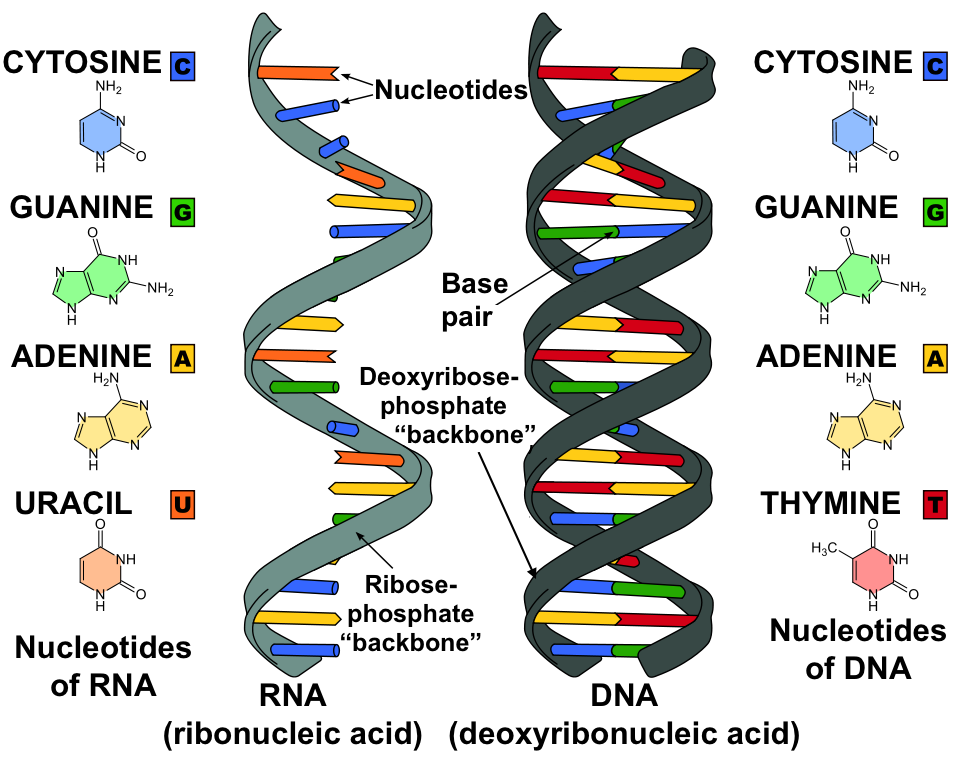
Segmented doublestranded RNA viruses structure and molecular biology Segmented doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) viruses are classifi ed into seven families comprising 24 genera This diverse group of viruses infect bacteria, fungi, protozoa, plants, molluscs, insects, arthropods, fi sh, birds, and mammals Viruses belonging to four genera, allThe chemical structure of RNA is very similar to that of DNA, but differs in three primary ways Unlike doublestranded DNA, RNA is a singlestranded molecule in many of its biological roles and consists of much While the sugarphosphate "backbone" of DNA contains deoxyribose, RNA contains ribose RNA 3 RNA (Ribonucleic acid ) RNA is a polymer of ribonucleotides linked together by 3'5' phosphodiester linkage 3 4 RNA V/S DNA Biochemistry For Medics 4 5 Differences between RNA and DNA SNo RNA DNA 1) Single stranded mainly except when self complementary sequences are there it forms a double stranded structure (Hair pin



What Is The Difference Between Dna And Double Stranded Rna Quora



Plos Biology Extensive Editing Of Cellular And Viral Double Stranded Rna Structures Accounts For Innate Immunity Suppression And The Proviral Activity Of Adar1p150
Secondary structure of RNA result from the formation of doublestranded RNA helices called RNA duplexes There are a number of these helices separated by singlestranded regions RNA helices are formed with the help of positively charged molecules in the environment that balance the negative charge of the RNA RNA MOLECULES typically exhibit extensive secondary structure, including doublestranded duplex, hairpins, internal loops, bulged bases and pseudoknotted1,2 structures (reviewed in refs 3 and 4)Monoclonal antibodies to doublestranded RNs probes of RNA structure in crude nucleic acid extracts JSchonborn, JOberstral3, EBreyel1, JTittgen2, JSchumacher2 and NLukacs*




The Chemical Structure Of Dna Compound Interest




Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
Structural Insight into the Mechanism of DoubleStranded RNA Processing by Ribonuclease III Jianhua Gan,1 Joseph E Tropea,1 Brian P Austin,1 Donald L Court,1 David S Waugh,1 and Xinhua Ji1,* 1Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Frederick, MD , USA *Contact jix@ncifcrfgov DOI /jcell4Compare the structure and functions of DNA and RNA View Answer A biology student uses a simple magnifier to examine the structural features of the wing of an insect The wing is held 350 cm in front of the lens, and the image is formed 250 cm from the eyeWe describe four monoclonal antibodies (MAB) which specifically recognize doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) together with their use in new methods for detecting and characterizing dsRNA in unfractionated nucleic acid extracts The specificity of the antibodies was analyzed using a panel of 27 different synthetic and naturally occurring nucleic acids
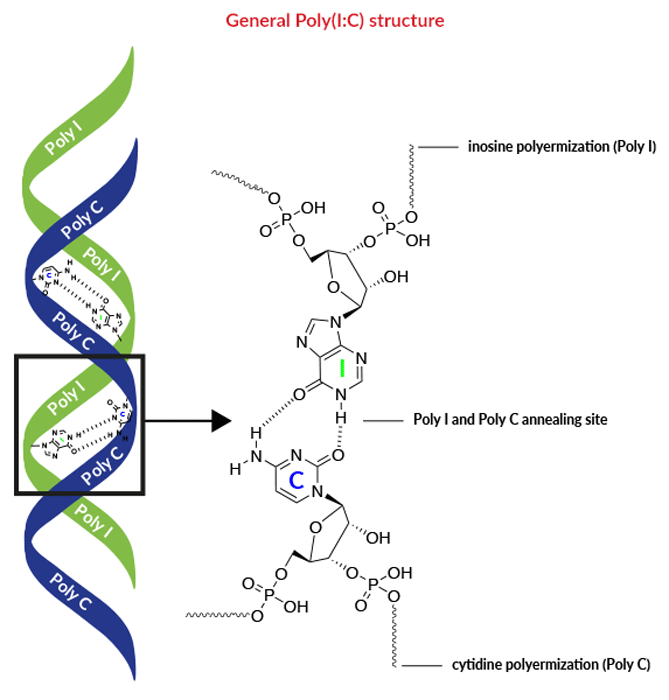



Tlr3 Ligands Synthetic Dsrna Poly I C Invivogen




Double Stranded Rna Bending By Au Tract Sequences Biorxiv
Secondary structural motifs of RNA are composed of single and doublestranded regions Doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) participates in the antiviral functions of the interferoninduced protein kinase PKR, gene regulation, and gene silencing, or RNA interference (RNAi) ()Thus, it is important to have accurate methods for identifying doublestranded segments of RNAOver the past decade our doublestranded RNA (dsRNA)antibodies have been used extensively to detect and characterise plant and animal viruses with dsRNA genomes or intermediates In addition, the antidsRNA antibodies can be used as a diagnostic tool to detect pathogens, including detection in paraffinembedded fixed tissue samples (Richardson et al 10)Differences between RNA and DNA SNo RNA DNA 1) Single stranded mainly except Double stranded (Except for when self complementary certain viral DNA s which are sequences are there it forms a single stranded) double stranded structure (Hair pin structure) 2) Ribose is the main sugar The sugar moiety is deoxy ribose 3) Pyrimidine components differ
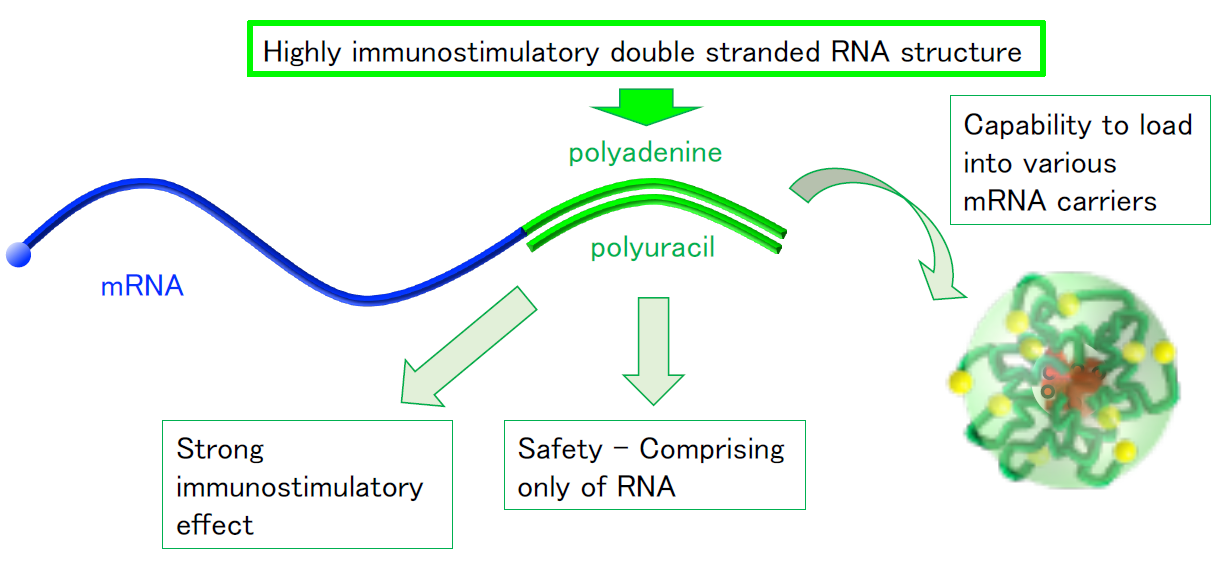



New Dual Function Vaccine Design The University Of Tokyo
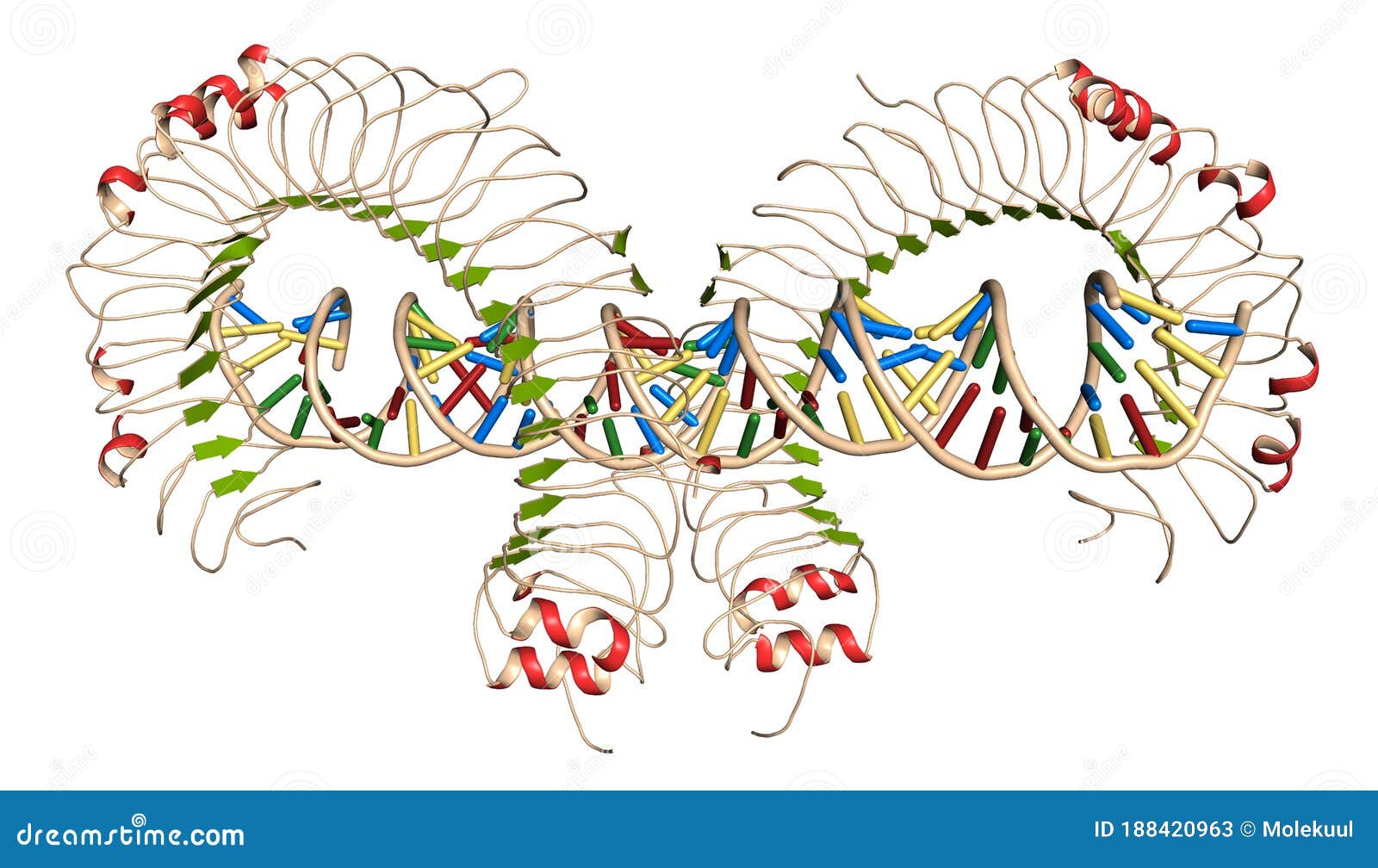



Toll Like Receptor 3 Tlr3 Murine Ectodomain Protein Bound To Double Stranded Rna Involved In Host Defense Against Viruses Stock Illustration Illustration Of Doublestranded Cd2
Doublestranded RNA viruses are a polyphyletic group of viruses that have doublestranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid The doublestranded genome is used to transcribe a positivestrand RNA by the viral RNAdependent RNA polymerase The positivestrand RNA may be used as messenger RNA which can be translated into viral proteins by the host cell's ribosomes The positivestrand RNA can also be replicated by the RdRp to create a new doublestranded viral genome DoublestrandedThomis et al, 1992), Drosophila staufen protein (St Johnston et al, 1991),DNA is amazing!!You guys can get in touch with me here and also ask your doubtshttps//wwwinstagramcom/seal_1school/?hl=enPray to God and Stay happy every
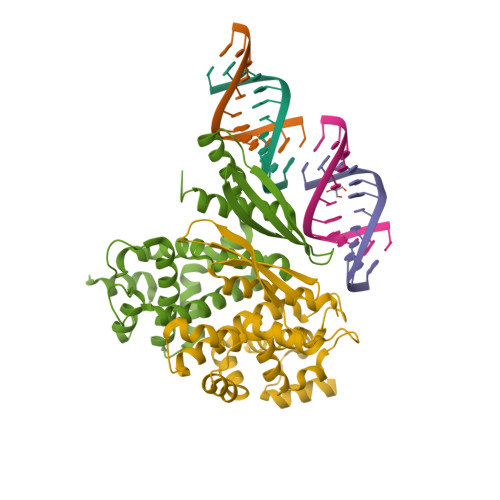



Rcsb Pdb 1yyk Crystal Structure Of Rnase Iii From Aquifex Aeolicus Complexed With Double Stranded Rna At 2 5 Angstrom Resolution




Pdf Structural Insight Into The Mechanism Of Double Stranded Rna Processing By Ribonuclease Iii Semantic Scholar
Population Structure of DoubleStranded RNA Mycoviruses That Infect the Rice Blast Fungus Magnaporthe oryzae in Japan Yuta Owashi 1 ,2 , Mitsuhiro Aihara 1 , Hiromitsu Moriyama 1 , Tsutomu Arie 1 , Tohru Teraoka 1 and Ken Komatsu 1 * Doublestranded DNA (dsDNA) and RNA (dsRNA) helices display an unusual structural diversity Some structural variations are linked to sequence and may serve as signaling units for proteinbinding partners Therefore, elucidating the mechanisms and factors that modulate these variations is of fundamental importance While the structural diversity of dsDNA has been The RNA double helix is a ubiquitous structural motif in living organisms Double stranded RNA is created by a number of biosynthetic pathways and is subsequently degraded, denatured, or specifically modified by enzymatic activities It also serves as a stable repository of genetic information for many viruses



Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology




Structure And Double Stranded Rna Binding Activity Of The Birnavirus Drosophila X Virus Vp3 Protein Journal Of Virology
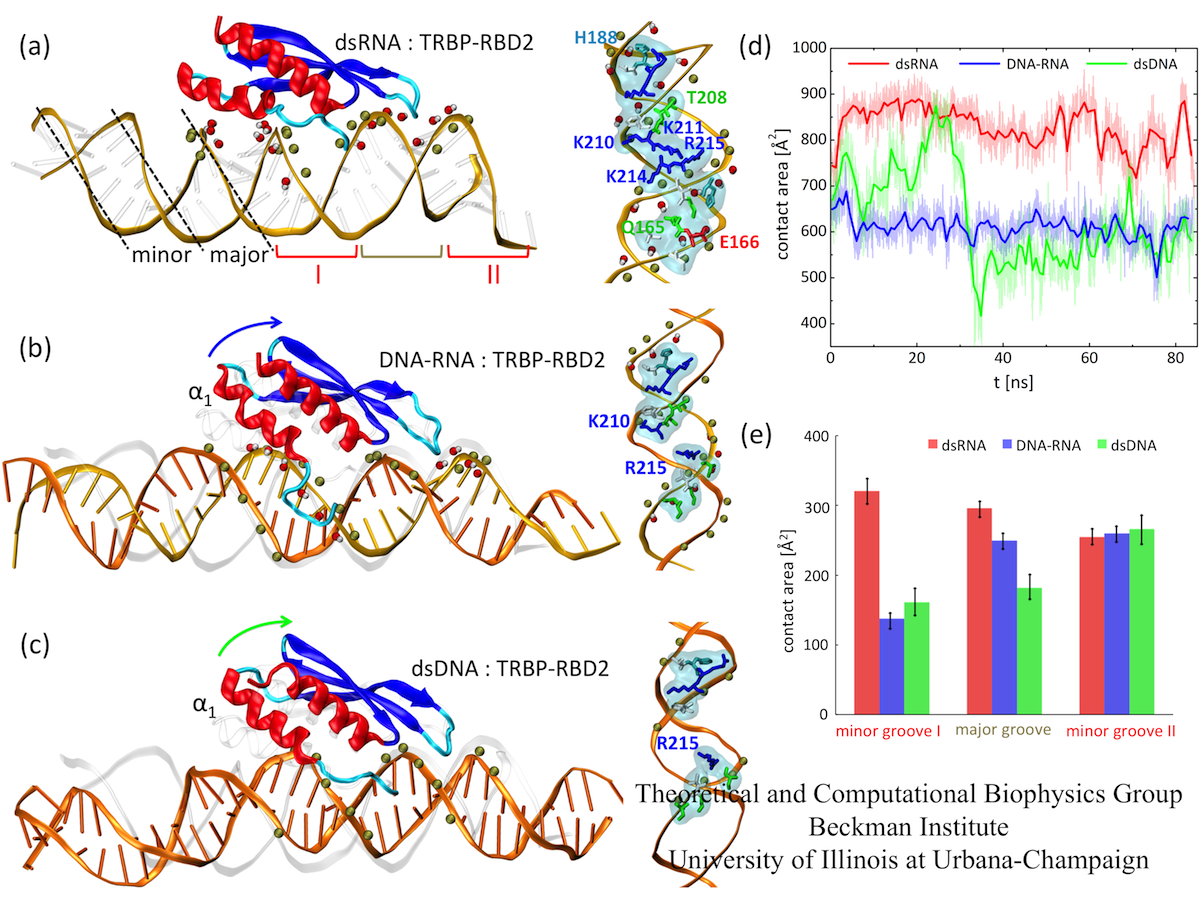
The TAR RNAbinding Protein (TRBP) is a doublestranded RNA (dsRNA)binding protein, which binds to Dicer and is required for the RNA interference pathway TRBP consists of three dsRNAbinding domains (dsRBDs) The first and second dsRBDs (dsRBD1 and dsRBD2, respectively) have affinities for dsRNA, whereas the third dsRBD (dsRBD3) binds to Dicer Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) (a) DNA is typically double stranded, whereas RNA is typically single stranded (b) Although it is single stranded, RNA can fold upon itself, with the folds stabilized by short areas of complementary base pairing within the molecule, forming a threedimensional structureEP 0401 DOUBLESTRANDED OLIGO RNA STRUCTURE COMPRISING MICRORNA origin EPA1 The present invention relates to a doublestranded oligo RNA structure comprising doublestranded miRNA, and a composition for preventing or treating cancer, containing the same More specifically, the present invention




Why Is Dna Double Stranded And Rna Single Stranded Biology Stack Exchange



Types Of Rna Mrna Rrna And Trna
Endogenous RNA transcription characterizes doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) viruses in the Reoviridae, a family that is exemplified by its simple, singleshelled member cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) (a) DNA is typically double stranded, whereas RNA is typically single stranded (b) Although it is single stranded, RNA can fold upon itself, with the folds stabilized by short areas of complementary base pairing within the molecule, forming a threedimensional structure Segmented doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) viruses are classified into seven families comprising 24 genera This diverse group of viruses infect bacteria, fungi, protozoa, plants, molluscs, insects, arthropods, fish, birds, and mammals Viruses belonging to four genera, all within the family reoviridae (orthoreoviruses, rotaviruses, orbiviruses, and coltiviruses), include viruses




The Nucleic Acid Dyah Kinasih Wuragil Veterinary Medicine




Double Stranded Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Structure and specific RNA binding of ADAR2 doublestranded RNA binding motifs Adenosine deaminases that act on RNA (ADARs) siteselectively modify adenosines to inosines within RNA transcripts, thereby recoding genomic information How ADARs select specific adenosine moieties for deamination is poorly understoodDoublestranded DNA and RNA, and DNA/RNA hybrids form naturally in cells between two nucleic acid strands containing complementary sequences However, these doublestranded nucleic acid structures need to be separated for DNA replication, RNA Doublestranded RNA drives SARSCoV2 nucleocapsid protein to undergo phase separation at specific temperatures Christine A Roden , Yifan Dai , Ian Seim , Myungwoon Lee , Rachel Sealfon , Grace A McLaughlin , Mark A Boerneke , Christiane Iserman , Samuel A Wey , Joanne L Ekena , Olga G Troyanskaya , Kevin M Weeks , Lingchong You , Ashutosh Chilkoti ,




Structure Of Dna And Rna




Functional Characterization Of And Cooperation Between The Double Stranded Rna Binding Motifs Of The Protein Kinase Pkr Journal Of Biological Chemistry
Unlike doublestranded helical structure of DNA, the RNAs are singlestranded RNA is an unbranched linear polymer of ribonucleotides joined by 3′, 5′ phosphodiester bonds The phosphodiester bonds join with the 3′ OH group of ribose of one nucleotide group to the 5′ OH group of ribose sugar of the next nucleotideTherefore AtoI editing events in coding sequences may result in recoding geneticThe 23m long human genome consists of 46 chromosomes, each of which is a single, long DNA molecule




Figure 3 From Black Sheep That Don T Leave The Double Stranded Rna Binding Domain Fold Semantic Scholar
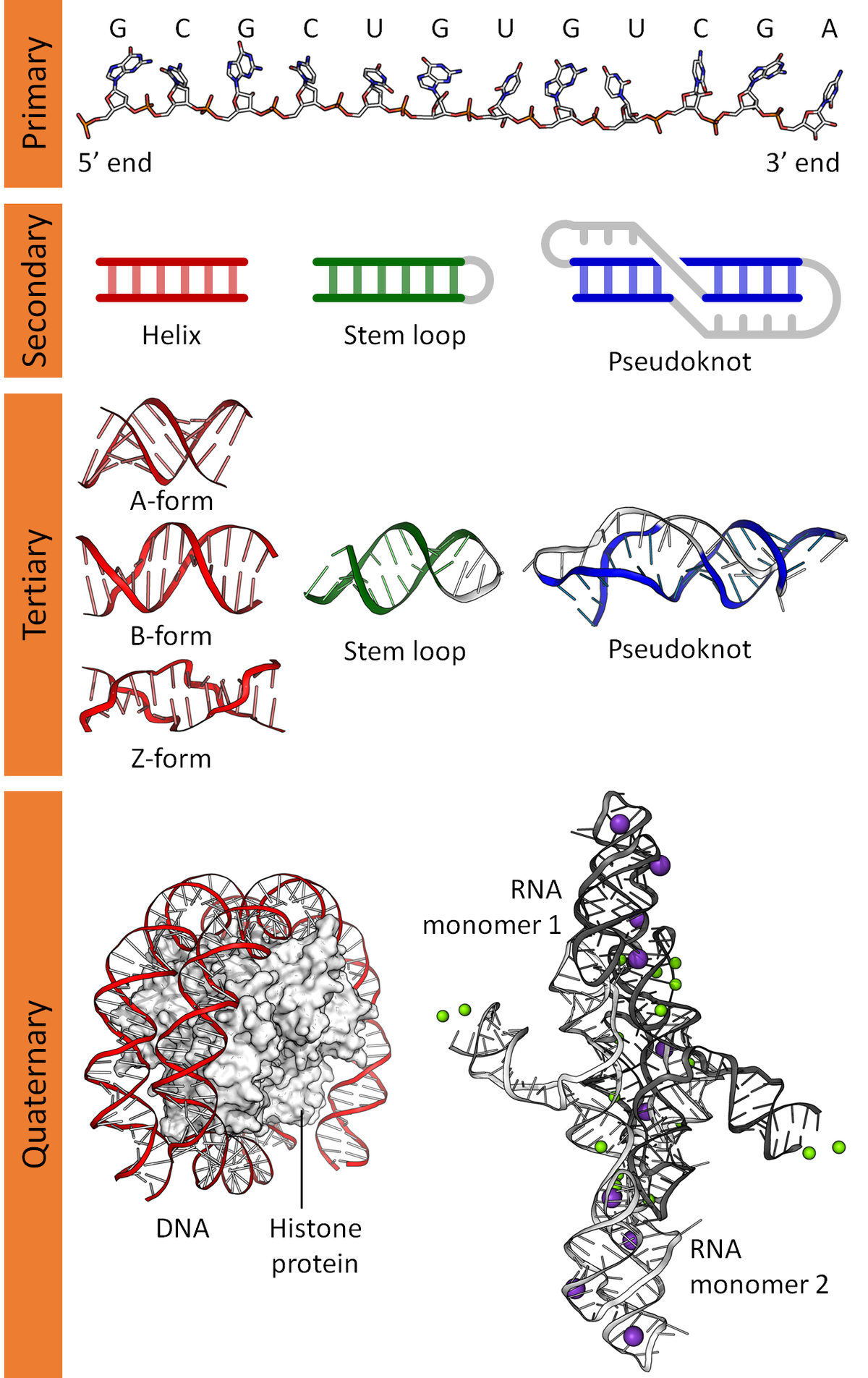



Nucleic Acid Structure Wikipedia
The doublestranded RNAbinding domain (dsRBD) is a 6570 amino acid sequence/structure motif that mediates dsRNA interactions in a large variety of proteins (St Johnston et al, 1992) such as the dsRNAdependent protein kinase PKR (Meurs et al, 1990;Double stranded ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a unique form of RNA that appears with two complementary strands, instead of a single strand in isolation, as is more common for this genetic material RNA contains the code for a number of biological activities and plays an important role in living organismsDoublestranded RNA (dsRNA) ELISA kit containing the following reagents for 0 tests (2x96 wells) • Reagent 01 1 vial of coating antibody (store at C) • Reagent A 1 vial of 142 bp dsRNA as positive control (store at C) • Reagent B 1 vial of dsRNAspecific detecting antibody (in RPMI 5% FBS, store at 4 °C or, preferably, at °C) • Reagent C 1 vial of HRPconjugated




Lesson Explainer Types Of Rna Nagwa




Rna Double Helix Structure Identified Using Synchrotron Newsroom Mcgill University
The doublestranded RNA binding domain (dsRBD) is an approximately 65 amino acid motif that is found in a variety of proteins that interact with doublestranded (ds) RNA, such as Escherichia coli RNase III and the dsRNAdependent kinase, PKR Drosophila staufen protein contains five copies of this motif, and the third of these binds dsRNA in vitro




Pyridazine Nucleobase In Triplex Forming Pna Improves Recognition Of Cytosine Interruptions Of Polypurine Tracts In Rna Acs Chemical Biology X Mol
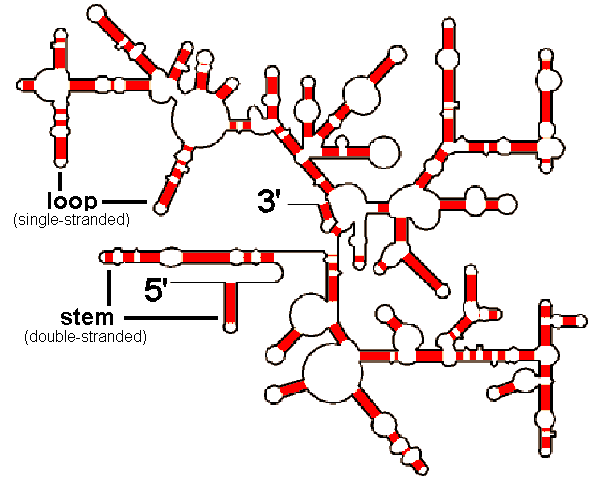



Stems Loops In Rrna
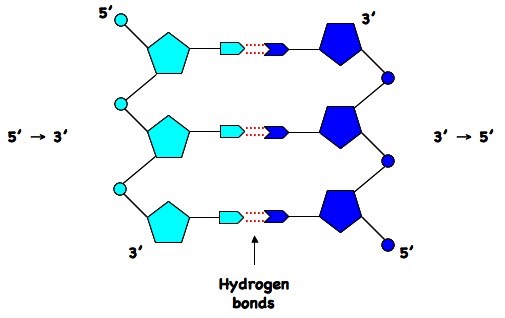



Dna Structure Bioninja



Plos Biology Extensive Editing Of Cellular And Viral Double Stranded Rna Structures Accounts For Innate Immunity Suppression And The Proviral Activity Of Adar1p150



Plos Biology Extensive Editing Of Cellular And Viral Double Stranded Rna Structures Accounts For Innate Immunity Suppression And The Proviral Activity Of Adar1p150




Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
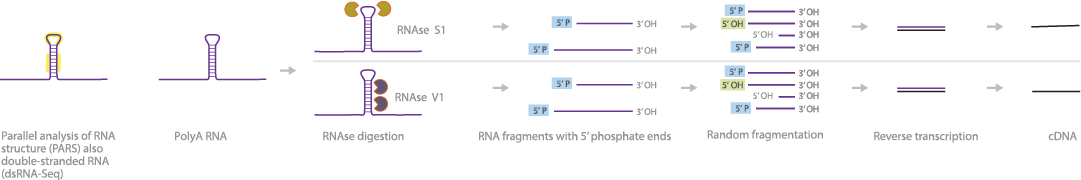



Pars Dsrna Seq



Structure Reactivity In Chemistry Ib3 Imf Nucleic Acids
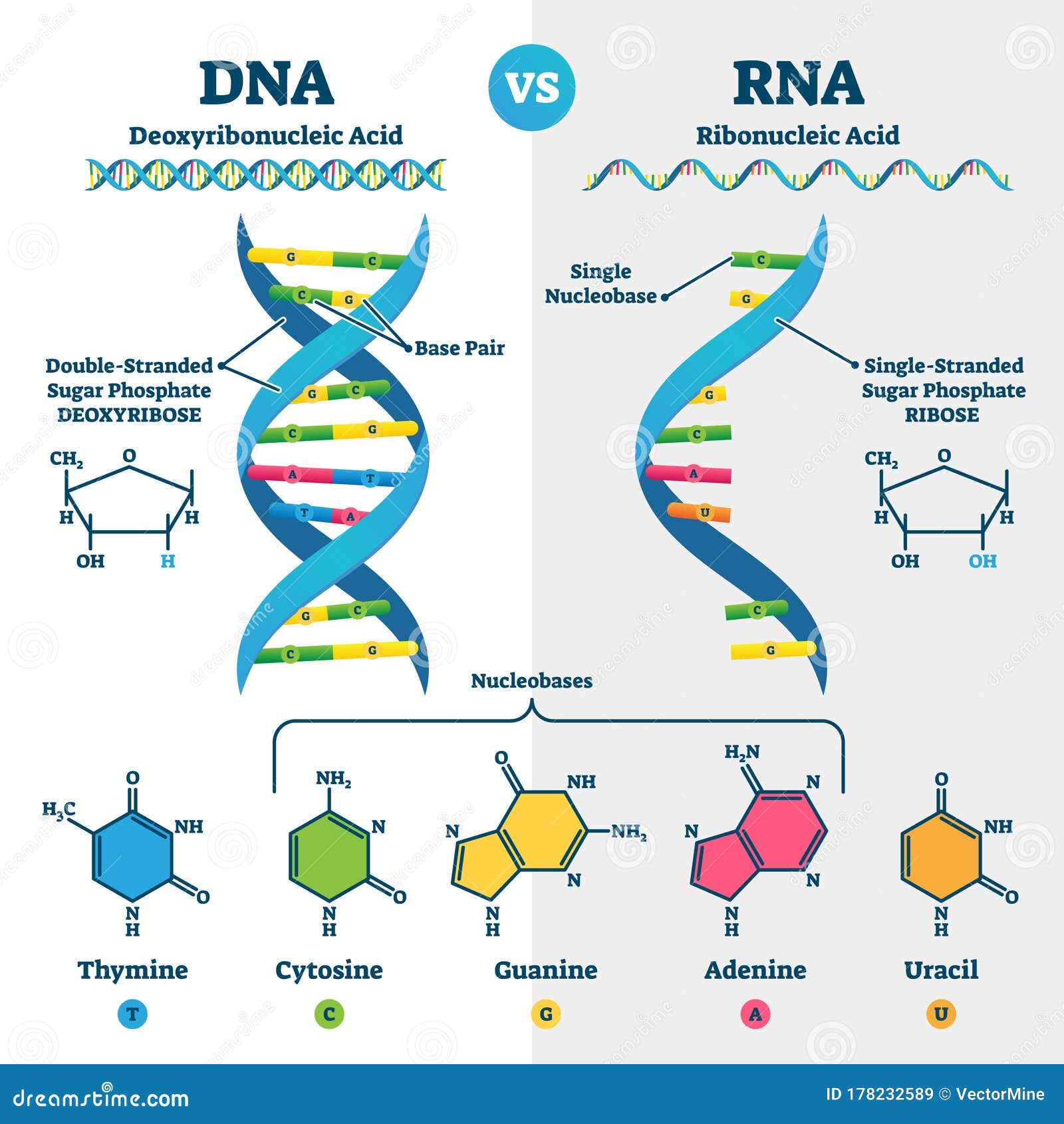



Rna Stock Illustrations 7 399 Rna Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Double Stranded Rna Binding Motif Dsrbm And Related Structures A Download Scientific Diagram



Double Stranded Rna Recognition In Gene Silencing Pathway
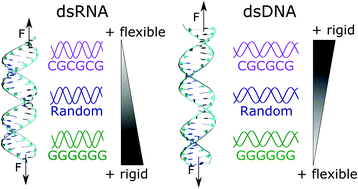



Sequence Dependent Mechanical Properties Of Double Stranded Rna Nanoscale Rsc Publishing




Nmr Structure Of A Classical Pseudoknot Interplay Of Single And Double Stranded Rna Science




Structural Basis For Cytosolic Double Stranded Rna Surveillance By Human Oligoadenylate Synthetase 1 Pnas




Molecular Basis Of Double Stranded Rna Protein Interactions Structure Of A Dsrna Binding Domain Complexed With Dsrna The Embo Journal




Rna Wikipedia



1



Rna And Protein Synthesis Review Article Khan Academy




Dna Vs Rna Differences Similarities Expii



1



Rcsb Pdb 1yyw Crystal Structure Of Rnase Iii From Aquifex Aeolicus Complexed With Double Stranded Rna At 2 8 Angstrom Resolution




Understanding The Mechanical Response Of Double Stranded Dna And Rna Under Constant Stretching Forces Using All Atom Molecular Dynamics Pnas



2 The Basic Structure Of Dna And Rna Dna Is Double Stranded Whereas Download Scientific Diagram



Rna Secondary Structure




A Novel Paperclip Double Stranded Rna Structure Demonstrates Clathrin Independent Uptake In The Mosquito Aedes Aegypti Insect Biochemistry And Molecular Biology X Mol




Structure And Function Of Rna Microbiology




Figure 4 From The Double Stranded Rna Binding Motif Interference And Much More Semantic Scholar
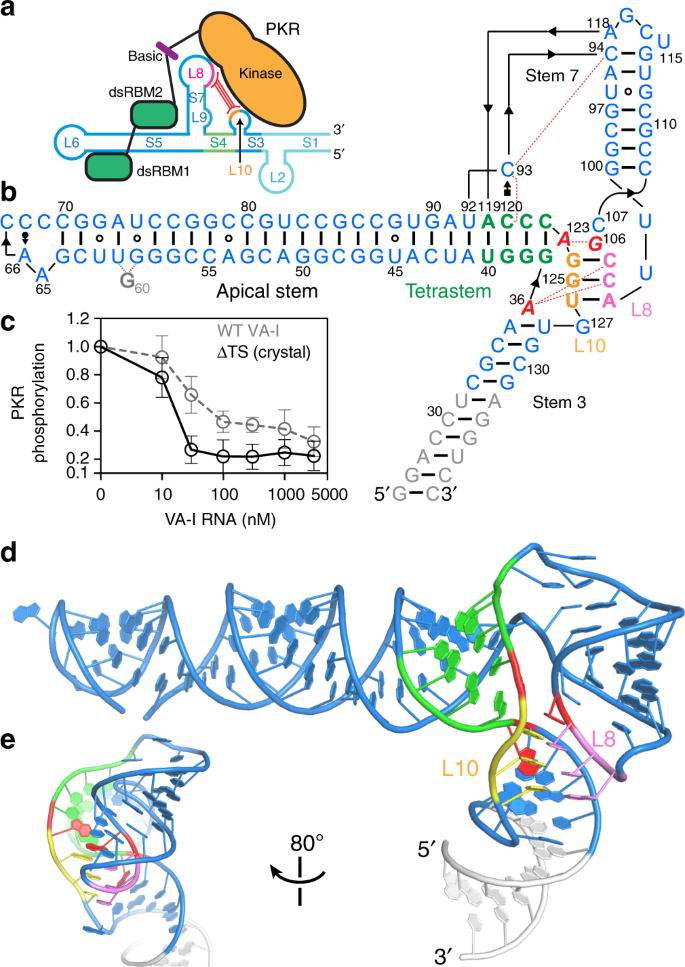



Crystal Structure Of An Adenovirus Virus Associated Rna Nature Communications



Double Stranded Rna High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Structure Of The Arabidopsis Thaliana Dcl4 Duf2 Domain Reveals A Noncanonical Double Stranded Rna Binding Fold For Protein Protein Interaction



Q Tbn And9gcsgw4hfn7dyrzq55rvhz4rpygjuz5kl9fpxr9k2rv8 Usqp Cau




Crystallographic And Modeling Studies Of Rnase Iii Suggest A Mechanism For Double Stranded Rna Cleavage Center For Cancer Research National Cancer Institute




Rna Wikipedia
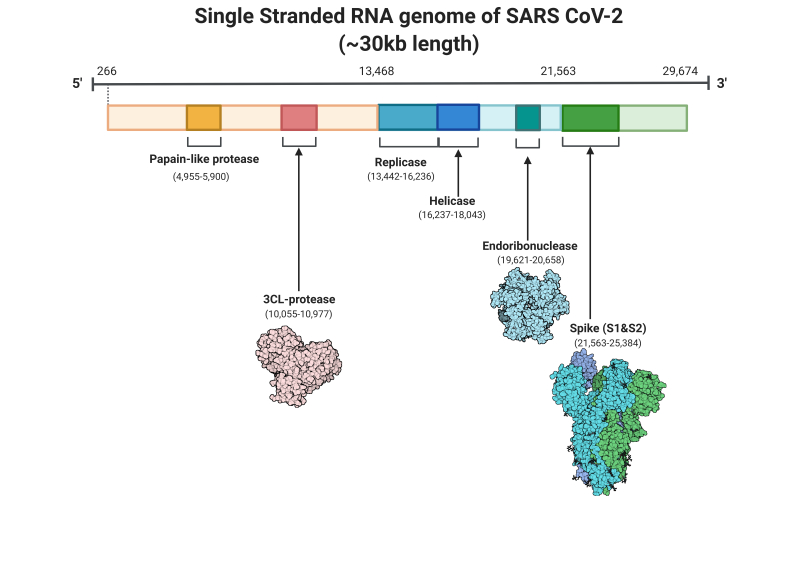



Figure Single Stranded Rna Genome Of Sars Cov2 Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf




Double Stranded Rna Under Force And Torque Similarities To And Striking Differences From Double Stranded Dna Pnas




Why Is Rna Single Stranded In General And Not Double Stranded Like Dna Quora




Segmented Double Stranded Rna Viruses Structure And Molecular Biology The Lancet Infectious Diseases




Nucleic Acid Structure Wikiwand
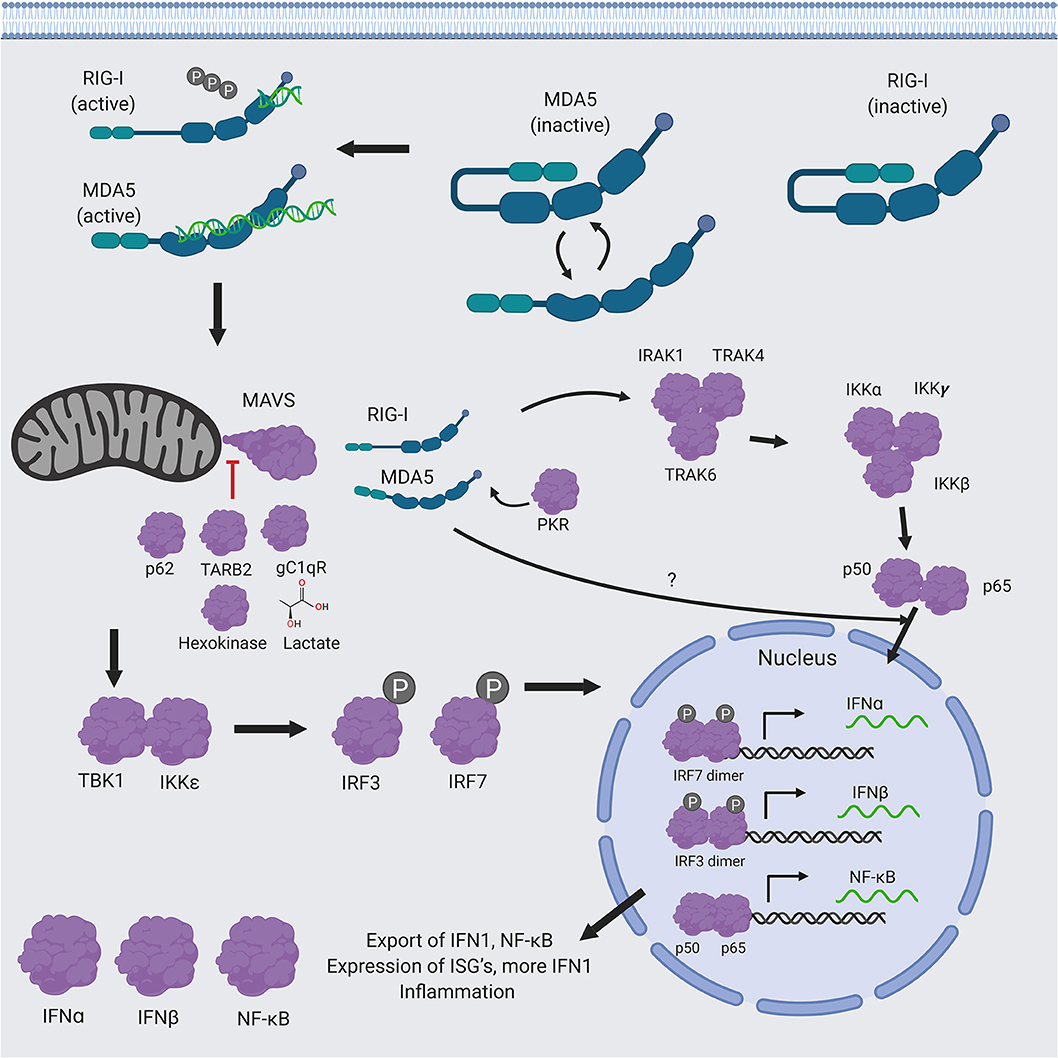



Frontiers Comparative Structure And Function Analysis Of The Rig I Like Receptors Rig I And Mda5 Immunology



Bacteriophage Phi6 Virus Capsid Computer Model Showing The Structure Of A Double Stranded Rna Virus Bacteriophage Phi6 Capsid Stock Photo Alamy
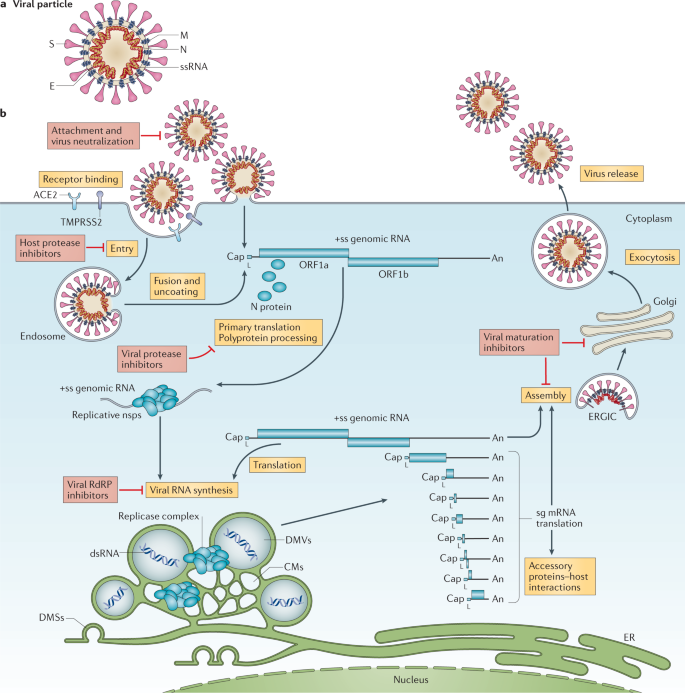



Coronavirus Biology And Replication Implications For Sars Cov 2 Nature Reviews Microbiology




Structures And Axis Curves For Ideal Dsdna And Dsrna Left Dna Right Download Scientific Diagram
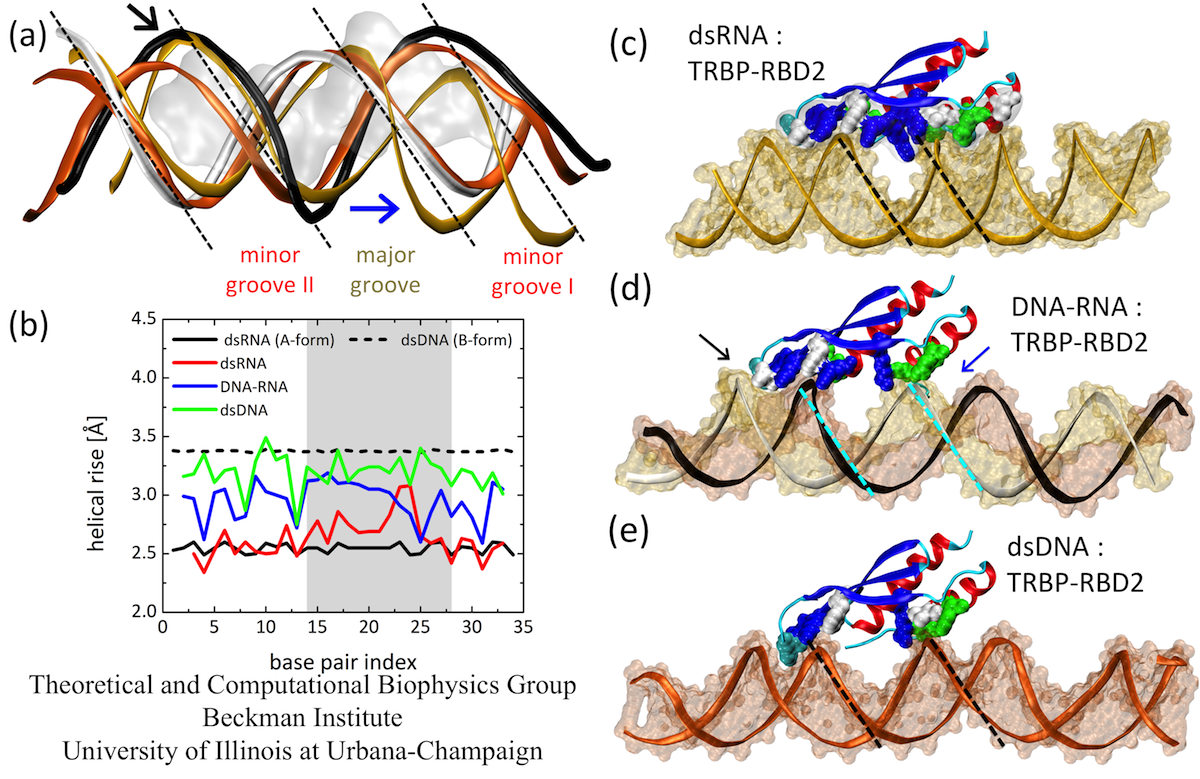



Double Stranded Rna Recognition In Gene Silencing Pathway




Characterization Of The Solution Complex Between The Interferon Induced Double Stranded Rna Activated Protein Kinase And Hiv I Trans Activating Region Rna Journal Of Biological Chemistry



Cryphonectria Nitschkei Virus 1 Structure Shows That The Capsid Protein Of Chrysoviruses Is A Duplicated Helix Rich Fold Conserved In Fungal Double Stranded Rna Viruses
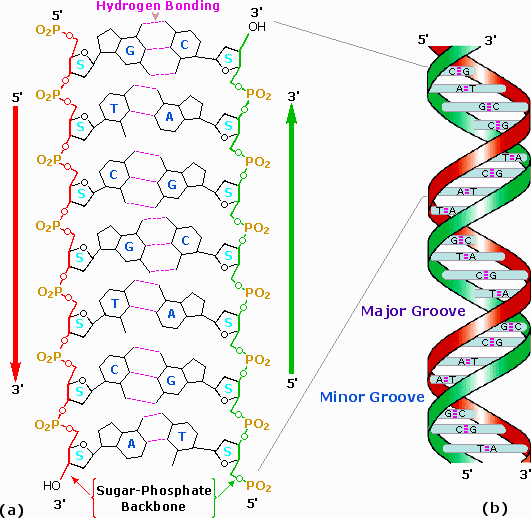



Nucleic Acids
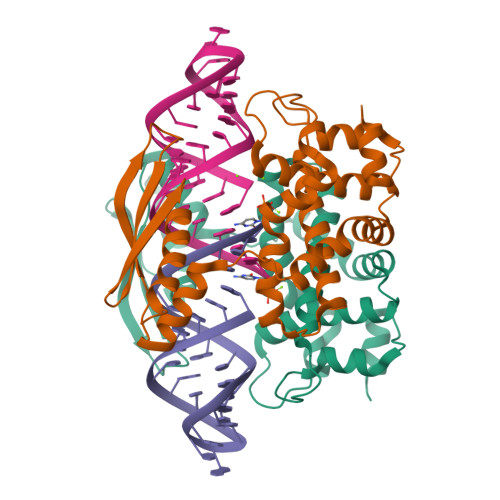



Rcsb Pdb 4m2z Crystal Structure Of Rnase Iii Complexed With Double Stranded Rna And Cmp Type Ii Cleavage



Monoclonal Antibodies To Double Stranded Rna As Probes Of Rna Structure In Crude Nucleic Acid Extracts Abstract Europe Pmc




The Structure Of Dsrna Binding Proteins A The Domain Structure Of Download Scientific Diagram



1




Cas13 Zhang Lab
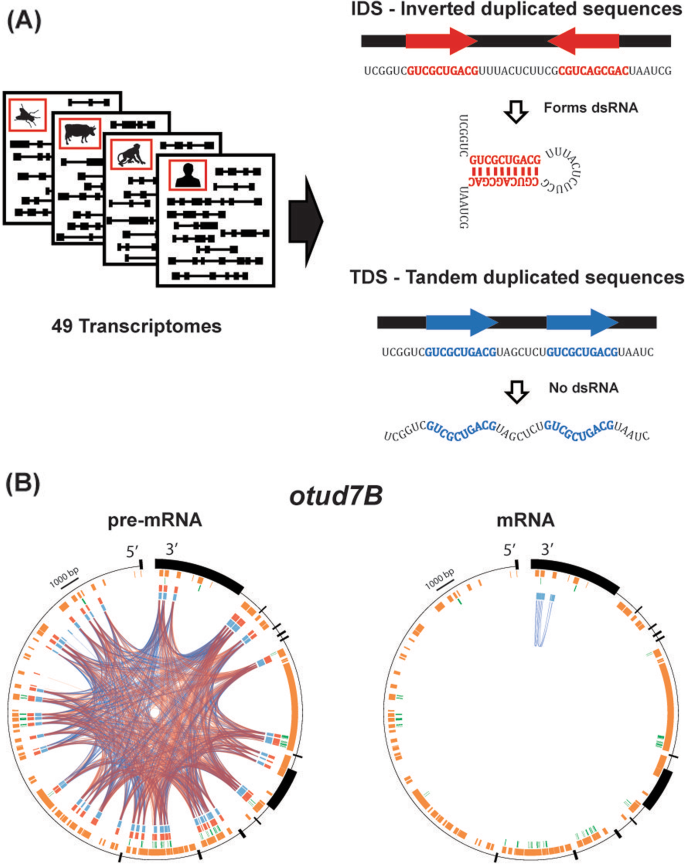



Purifying Selection Of Long Dsrna Is The First Line Of Defense Against False Activation Of Innate Immunity Genome Biology Full Text




Iv Nuclear Biochemistry 4 2 Nucleic Acids 4




Fig 4 Structural Basis For Double Stranded Rna Processing By Dicer Science
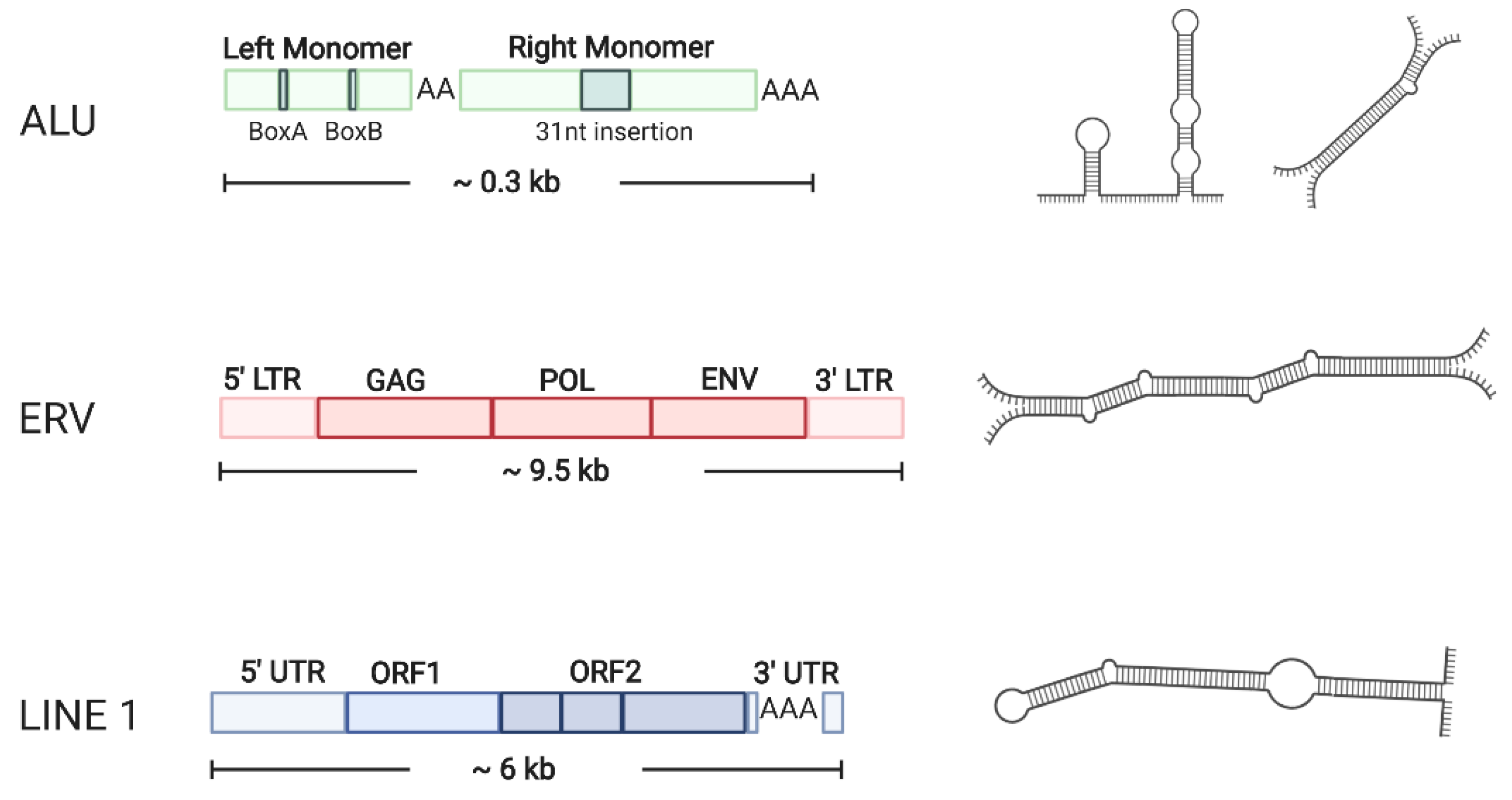



Ncrna Free Full Text Endogenous Double Stranded Rna Html




Double Stranded Rna Single Stranded Dna Biology Stack Exchange




Double Stranded Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Rna Integrity And Quantification



Www Cell Com Biophysj Pdf S0006 3495 18 3 Pdf




Double Stranded Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Structure And Specific Rna Binding Of Adar2 Double Stranded Rna Binding Motifs Structure




Double Stranded Rna Biochemistry Britannica




Origins And Evolution Of The Global Rna Virome Mbio
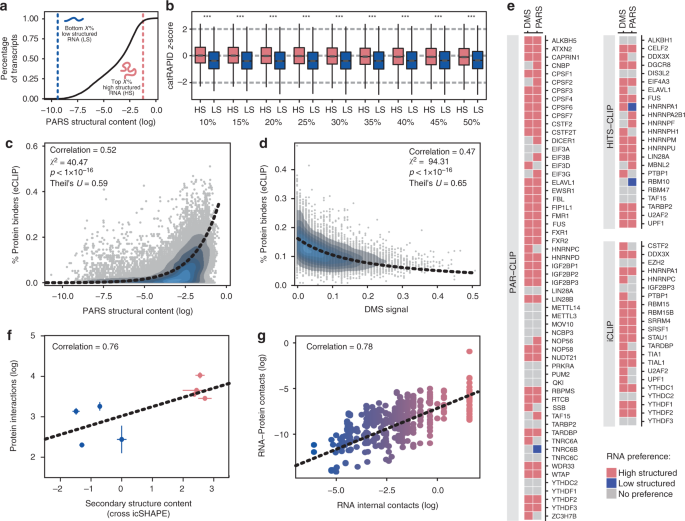



Rna Structure Drives Interaction With Proteins Nature Communications
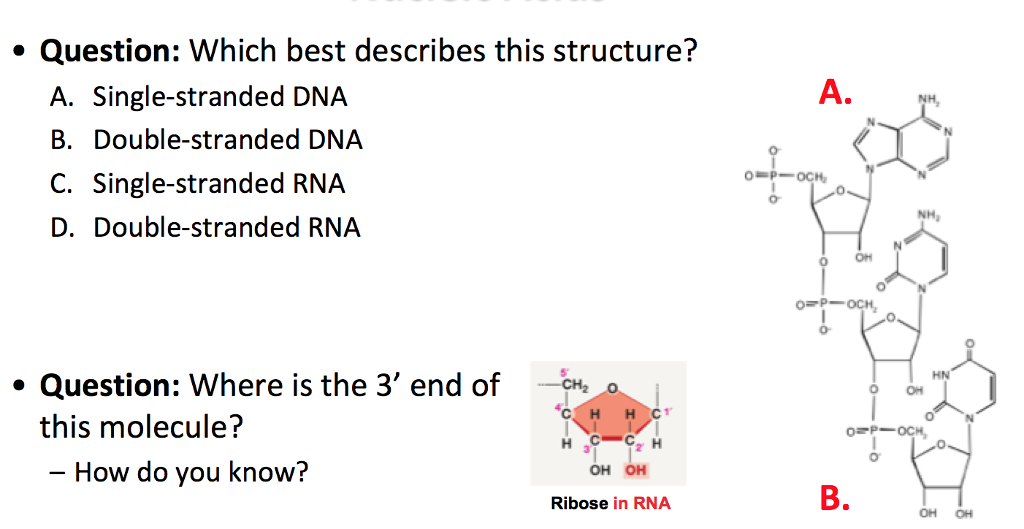



Question Which Best Describes This Structure A Chegg Com




Rna Structure Rna Seq Blog




What Is Double Stranded Rna With Pictures




Segmented Double Stranded Rna Viruses Structure And Molecular Biology
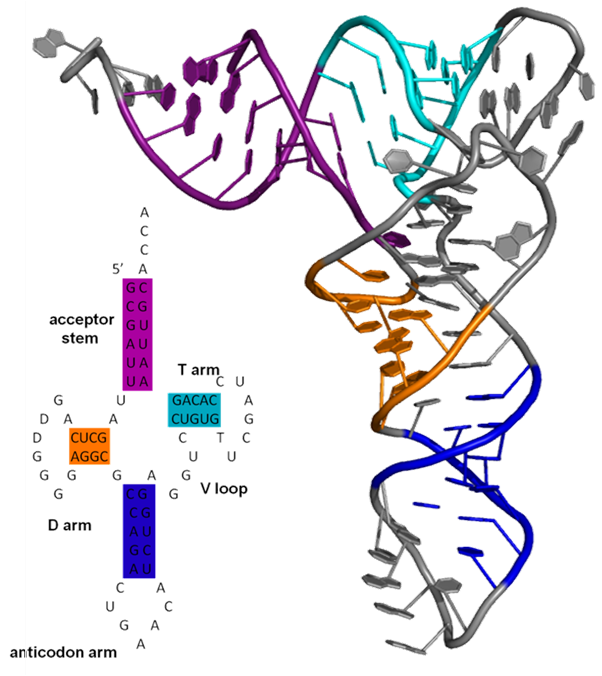



Rna Biomacromolecular Structures
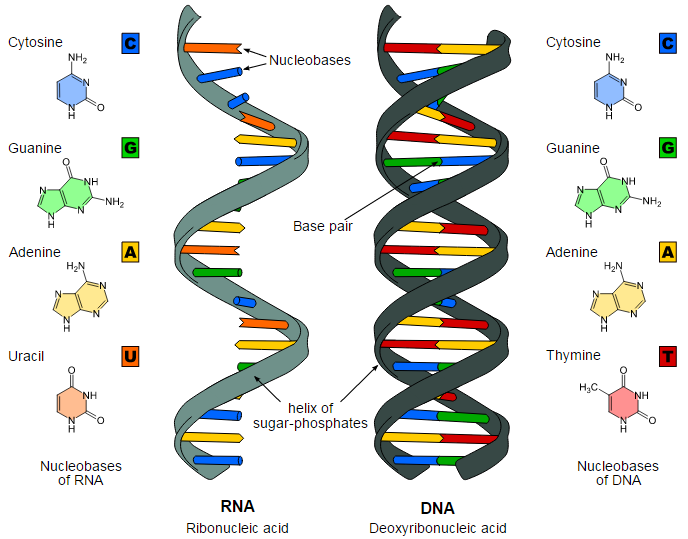



What Are The Similarities Between Dna And Rna Albert Io




Human Nlrp1 Is A Sensor For Double Stranded Rna Science




Rna Interference Overview Abcam
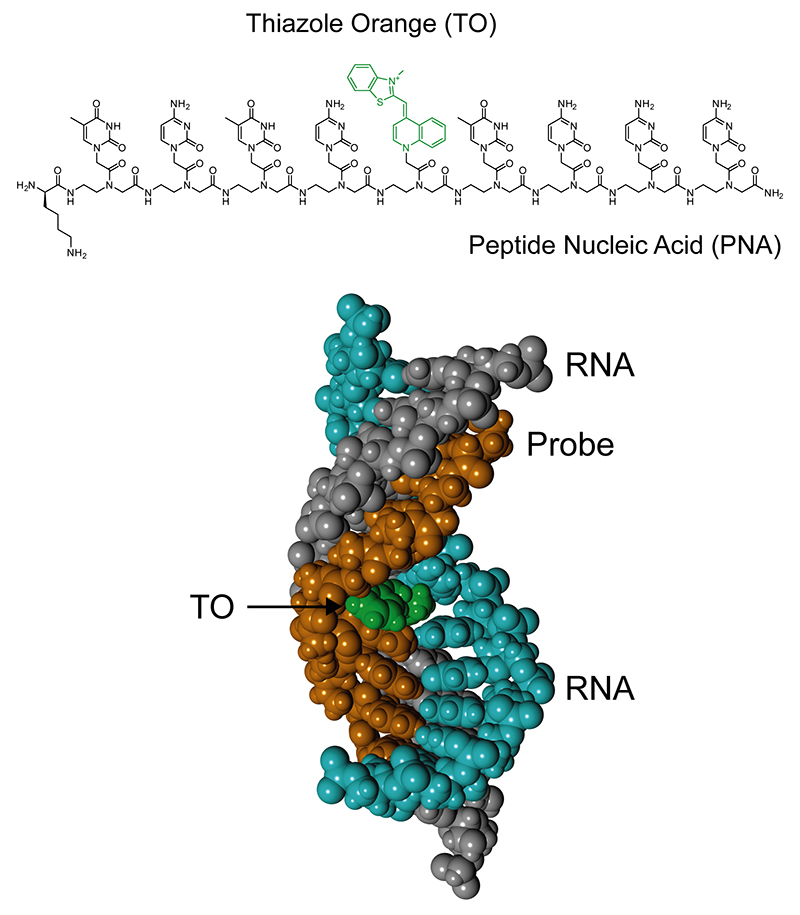



Research News New Analytical Tool For Fluorescence Detection Of Double Stranded Rna Tohoku University Global Site




Segmented Double Stranded Rna Viruses Structure And Molecular Biology Patton John T Amazon Com Books




Structure Of Hiv 1 Rt Dsrna Initiation Complex Prior To Nucleotide Incorporation Pnas
/dna-versus-rna-608191_sketch_Final-54acdd8f8af04c73817e8811c32905fa.png)



The Differences Between Dna And Rna



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿